Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in antiphospholipid antibody positive patients with high risk of miscarriage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39494295
- PMCID: PMC11531756
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18419
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in antiphospholipid antibody positive patients with high risk of miscarriage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of the present study was to evaluate whether intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) increases live birth rates and improves neonatal results in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) at high-risk for miscarriage.
Background: Positivity of aPL in pregnant women is a high-risk factor for miscarriage, and IVIG treatment has emerged as a potential intervention.
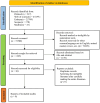
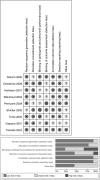
Methods: The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline was employed to search multiple electronic databases for articles published until August 20, 2023, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus and Medline. The inclusion criteria encompassed studies assessing the efficacy of IVIG in aPL-positive patients with a high risk of miscarriage. Relevant articles were assessed for the quality and data were extracted for analysis. Two independent reviewers performed study selection, data extraction, and quality assessments. The risk of bias was evaluated according to the Cochrane risk of bias tool. All analyses were conducted using Review Manager 5.3.
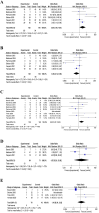
Results: This systematic review included nine randomized controlled trials, with 366 aPL-positive women at high risk of miscarriage. These studies included in this review were randomized controlled trials. The primary outcome measures were successful pregnancy outcomes and live birth rates. The secondary outcomes included obstetric complications, and neonatal outcomes (such as birth weight and live-birth rate). The comparison between the intervention and control groups revealed no significant differences in terms of obstetric complications and neonatal outcomes. The group receiving IVIG treatment had a higher prevalence of preterm deliveries than controls (OR = 2.05, I2 = 46%, 95% CI [0.58-5.24]), but also exhibited a partial improvement in live birth rates (OR = 2.86, I2 = 52%, 95% CI [1.04-7.90]), because it reduced the number of miscarriages (OR = 0.35, I2 = 52%, 95% CI [0.13-0.96]).
Conclusion: Based on the available evidence, IVIG intervention appears to be a potentially effective approach for managing of aPL-positive pregnant women with high risk of miscarriage. While IVIG shows significant potential in tripling the chances of having a live-born child, further large-scale randomized controlled trials are necessary, preferably comparing IVIG with hydroxychloroquine or lifestyle and dietary interventions, to refine treatment protocols and ensure the most effective application.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid antibodies; Intravenous immunoglobulin; Miscarriage; Systematic review.
© 2024 Yuan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of Pregnancy Outcomes in Patients Exhibiting Recurrent Miscarriage With Concurrent Low-Titer Antiphospholipid Antibodies.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024 Nov;92(5):e13940. doi: 10.1111/aji.13940. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39469745
-
Progestogen for preventing miscarriage in women with recurrent miscarriage of unclear etiology.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 8;10(10):CD003511. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003511.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11). doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003511.pub5. PMID: 30298541 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Aspirin or heparin or both for improving pregnancy outcomes in women with persistent antiphospholipid antibodies and recurrent pregnancy loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 2;5(5):CD012852. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012852.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32358837 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial injection of embryo culture supernatant for subfertile women in assisted reproduction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 14;8(8):CD013063. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013063.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32797689 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of recurrent miscarriage in women with antiphospholipid syndrome: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lupus. 2021 Jan;30(1):70-79. doi: 10.1177/0961203320967097. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 33081590
Cited by
-
Non-Criteria Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Myth or Reality?J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 15;14(4):1299. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041299. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Patients with Recurrent Miscarriage: A Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2025 Jun;54(6):1193-1203. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v54i6.18897. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40655495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell Tolerance and Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Jun 8;68(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09064-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40483664 Review.
References
-
- Alijotas-Reig J, Esteve-Valverde E, Ferrer-Oliveras R, Sáez-Comet L, Lefkou E, Mekinian Aène, Belizna C, Ruffatti A, Tincani A, Marozio L, Espinosa G, Cervera R, Ríos-Garcés R, De Carolis S, Latino O, Lurba EL, Chighizola CB, Gerosa M, Pengo V, Lundelin K, Rovere-Querini P, Canti V, Mayer-Pickel K, Reshetnyak T, Hoxha A, Tabacco S, Stojanovich L, Gogou V, Varoudis A, Arnau A, Ruiz-Hidalgo D, Trapé J, Sos L, Stoppani C, Martí-Cañamares A, Farran-Codina I. The European Registry on Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome (EUROAPS): a survey of 1000 consecutive cases. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2019;18(4):406–414. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.12.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andreoli L, Bertsias GK, Agmon-Levin N, Brown S, Cervera R, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Doria A, Fischer-Betz R, Forger F, Moraes-Fontes MF, Khamashta M, King J, Lojacono A, Marchiori F, Meroni PL, Mosca M, Motta M, Ostensen M, Pamfil C, Raio L, Schneider M, Svenungsson E, Tektonidou M, Yavuz S, Boumpas D, Tincani A. EULAR recommendations for women’s health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017;76(3):476–485. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209770. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnout J, Spitz B, Wittevrongel C, Vanrusselt M, Van Assche A, Vermylen J. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of a pregnant patient with an antiphospholipid syndrome: immunological changes associated with a successful outcome. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 1994;71(6):741–747. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1642516. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

