Targeting Neurological Disorders with Stilbenes: Bridging the Preclinical-Clinical Gap
- PMID: 39494329
- PMCID: PMC11528462
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.102032
Targeting Neurological Disorders with Stilbenes: Bridging the Preclinical-Clinical Gap
Abstract
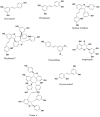
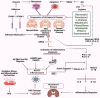
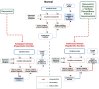
Neurological disorders (NDs) encompass a range of debilitating conditions that affect the nervous system, including prevalent illnesses such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and ischemic stroke. Despite significant ongoing studies, effective therapeutic strategies to halt or slow down the progression of these illnesses are still lacking. Stilbenes, a class of natural polyphenols, have shown potential as candidates for therapeutic strategies due to their capacity to protect the nervous system. Preclinical studies have provided strong evidence that stilbenes can regulate many cellular pathways implicated in neurodegeneration, with resveratrol being a well-studied compound that has shown the ability to reduce oxidative damage, promote neurogenesis, and enhance mitochondrial function - crucial for maintaining brain health. In preclinical animal models, initial research has also shown promise in additional substances such as piceatannol and pterostilbene. Furthermore, clinical studies have explored the therapeutic benefits of stilbenes in NDs. Despite promising results in preclinical research, the use of stilbenes in clinical trials is currently limited, with most studies focusing on resveratrol. Although several clinical studies have demonstrated the beneficial impact of resveratrol supplementation on brain health and degenerative consequences, other investigations have yielded ambiguous findings, underscoring the urgent need for more comprehensive and precisely planned clinical research. This study delves into the potential benefits of stilbenes as neuroprotective agents for NDs. It emphasizes the need for more clinical research to enhance our understanding of their therapeutic effectiveness in specific patient groups.
Keywords: Chemistry; Clinical studies; Neurological disorders; Preclinical studies; Stilbenes.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

