Reconstruction of the Hepatic Microenvironment and Pathological Changes Underlying Type II Diabetes through Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
- PMID: 39494341
- PMCID: PMC11528452
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.99176
Reconstruction of the Hepatic Microenvironment and Pathological Changes Underlying Type II Diabetes through Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
Abstract
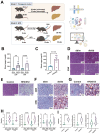
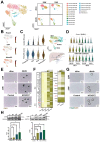
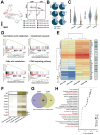
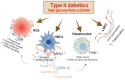
The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) continues to rise. Therefore, it has become a major concern health issue worldwide. T2DM leads to various complications, including metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). However, comprehensive studies on MAFLD as a diabetic complication at different stages are still lacking. Using advanced single-cell RNA-seq technology, we explored changes of livers in two T2DM murine models. Our findings revealed that increase activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) exacerbated the development of MAFLD to steatohepatitis by upregulating transforming growth factor β1 induced transcript 1 (Tgfb1i1). Upregulated thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) contributed to hepatocyte damage by impairing reactive oxygen species clearance. Additionally, the capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells correlated with Fabp4 overexpression in endothelial cells. A novel subset of Kupffer cells (KCs) that expressed Cd36 exhibited an activated phenotype, potentially participating in inflammation in the liver of diabetic mice. Furthermore, ligand-receptor pair analysis indicated that activated HSCs interacted with hepatocytes or KCs through Thbs2 and Lamb2 in late-stage diseases. The reduction in cell-cell interactions within hepatocytes in diabetic mice, reflects that the mechanisms regulating liver homeostasis is disrupted. This research underscores the importance of dynamics in diabetic MAFLD, and provides new insights for targeted therapies.
Keywords: Capillarization; MAFLD; T2DM; Tgfb1i1; Txnip.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M. et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10:284–296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

