Proteomic study of medicinal mushroom extracts reveals antitumor mechanisms in an advanced colon cancer animal model via ribosomal biogenesis, translation, and metabolic pathways
- PMID: 39494346
- PMCID: PMC11528127
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475102
Proteomic study of medicinal mushroom extracts reveals antitumor mechanisms in an advanced colon cancer animal model via ribosomal biogenesis, translation, and metabolic pathways
Abstract
Introduction: Colorectal cancer ranks as the third most common cancer in both men and women, with approximately 35% of cases being stage IV metastatic at diagnosis. Even with treatment advancements, the survival rates for these patients remain suboptimal. There is a significant focus on developing multi-targeted therapies due to the common issue of drug resistance in standard and targeted cancer treatments. Medicinal mushrooms, both as single compounds and as complex extracts, have undergone extensive research. Numerous types of mushrooms have been shown to be safe, effective inhibitors of cancer pathways and strong enhancers of the immune system.
Methods: In this study, we performed both qualitative and quantitative proteomic analyses using tandem mass tags (TMT) on CT26 wild type (CT26. WT) colon cancer tissues from Balb/c mice, which were treated with a special blend of medicinal mushroom extracts, either alone or in combination with the chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil.
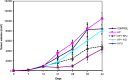
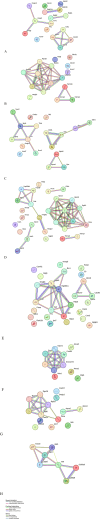
Results: The results showed a notable increase in survival rates and indicated that medicinal mushroom preparation Agarikon Plus, both alone and combined with 5-fluorouracil or another medicinal mushroom preparation Agarikon.1, impedes multiple key processes in colorectal cancer progression. The analysis of differentially expressed proteins in treated groups was done by use of bioinformatics tools and a decrease in ribosomal biogenesis (e.g., RPS3) and translation processes (e.g., RPL14) as well as an increase in unfolded protein response (e.g., DNAJC3), lipid metabolism (e.g., ACOT7), and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (e.g., FH) were observed.
Conclusion: The treatment induced various alterations of known biomarkers and protein clusters critical to the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer, laying a promising foundation for further translational research on this treatment modality.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; colorectal cancer; medicinal mushrooms; proteomics; translation; unfolded protein response.
Copyright © 2024 Jakopovic, Horvatić, Baranasic, Car, Oršolić, Jakopovich, Sedić and Kraljević Pavelić.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors BJ and IJ were employed by the company Dr Myko San Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment With Medicinal Mushroom Extract Mixture Inhibits Translation and Reprograms Metabolism in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Animal Model as Evidenced by Tandem Mass Tags Proteomics Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1202. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01202. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32973493 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor, Immunomodulatory and Antiangiogenic Efficacy of Medicinal Mushroom Extract Mixtures in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Animal Model.Molecules. 2020 Oct 28;25(21):5005. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215005. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33126765 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity of blended versus single medicinal mushroom extracts on human cancer cell lines: contribution of polyphenol and polysaccharide content.Int J Med Mushrooms. 2013;15(5):435-48. doi: 10.1615/intjmedmushr.v15.i5.20. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2013. PMID: 24266369
-
Proteomic Research on the Antitumor Properties of Medicinal Mushrooms.Molecules. 2021 Nov 5;26(21):6708. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216708. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of Medicinal Mushrooms in Integrative Oncology: A Narrative Review.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 11;11:580656. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.580656. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33424591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badalyan S., Rapior S. (2021). Agaricomycetes mushrooms (Basidiomycota) as potential neuroprotectants. Italian J. Mycol., 30–43. 10.6092/ISSN.2531-7342/12542 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

