Sestrin2 Attenuates Myocardial Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cardiac Dysfunction During Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 39494564
- PMCID: PMC11935719
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.035193
Sestrin2 Attenuates Myocardial Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cardiac Dysfunction During Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
Background: Sesn2 (Sestrin2) is a stress-induced protein that provides protective effects during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury, while endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress may be a pivotal mediator of I/R injury. The goal of this study was to determine whether Sesn2-mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling regulates ER stress during myocardial I/R.
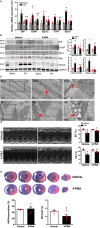
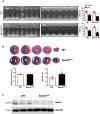
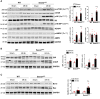
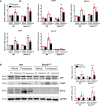
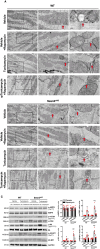
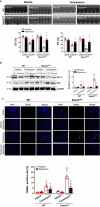
Methods and results: In vivo cardiac I/R was induced by ligation and subsequent release of the left anterior descending coronary artery in wild-type (WT) and cardiac-specific Sesn2 knockout (Sesn2cKO) mice. At 6 hours and 24 hours after reperfusion, cardiac function was evaluated, and heart samples were collected for analysis. I/R induced cardiac ER stress and upregulated Sesn2 mRNA and protein levels. Inhibiting ER stress with 4-phenylbutyric acid reduced infarct size by 37.5%, improved cardiac systolic function, and mitigated myocardial cell apoptosis post-I/R. Hearts from Sesn2cKO mice displayed increased susceptibility to ER stress during I/R compared with WT. Notably, cardiac mTOR signaling was further increased in Sesn2cKO hearts compared with WT hearts during I/R. In mice with cardiac Sesn2 deficiency, compared with WT, ER lumen was significantly expanded after tunicamycin-induced ER stress, as assessed by transmission electron microscopy. Additionally, pharmacological inhibition of mTOR signaling with rapamycin improved cardiac function after tunicamycin treatment and significantly attenuated the unfolded protein response and apoptosis in WT and Sesn2cKO mice.
Conclusions: Sesn2 attenuates cardiac ER stress post-I/R injury via regulation of mTOR signaling. Thus, modulation of the mTOR pathway by Sesn2 could be a critical factor for maintaining cardiac ER homeostasis control during myocardial I/R injury.
Keywords: cardiac injury; heart; mTOR signaling; unfolded protein response.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131:e29–e322. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000152 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

