A human monoclonal antibody neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants containing the L452R mutation
- PMID: 39494911
- PMCID: PMC11650997
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01223-24
A human monoclonal antibody neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants containing the L452R mutation
Abstract
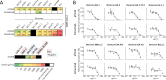
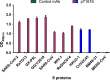
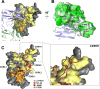
The effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic antibodies targeting the spike (S) receptor-binding domain (RBD) has been hampered by the emergence of variants of concern (VOCs), which have acquired mutations to escape neutralizing antibodies (nAbs). These mutations are not evenly distributed on the RBD surface but cluster on several distinct surfaces, suggesting an influence of the targeted epitope on the capacity to neutralize a broad range of VOCs. Here, we identified a potent nAb from convalescent patients targeting the receptor-binding domain of a broad range of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. Except for the Lambda and BA.2.86 variants, this nAb efficiently inhibited the entry of most tested VOCs, including Omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.2, XBB.1.5, and EG.5.1 and to a limited extent also BA.4/5, BA.4.6, and BQ.1.1. It bound recombinant S protein with picomolar affinity, reduced the viral load in the lung of infected hamsters, and prevented the severe lung pathology typical for SARS-CoV-2 infections. An X-ray structure of the nAb-RBD complex revealed an epitope that does not fall into any of the conventional classes and provided insights into its broad neutralization properties. Our findings highlight a conserved epitope within the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that should be preferably targeted by therapeutic antibodies and inform rational vaccine development.IMPORTANCETherapeutic antibodies are effective in preventing severe disease from SARS-CoV-2 infection and constitute an important option in pandemic preparedness, but mutations within the S protein of virus variants (e.g., a mutation of L452) confer resistance to many of such antibodies. Here, we identify a human antibody targeting the S protein receptor-binding domain (RBD) with an elevated escape barrier and characterize its interaction with the RBD functionally and structurally at the atomic level. A direct comparison with reported antibodies targeting the same epitope illustrates important differences in the interface, providing insights into the breadth of antibody binding. These findings highlight the relevance of an extended neutralization profiling in combination with biochemical and structural characterization of the antibody-RBD interaction for the selection of future therapeutic antibodies, which may accelerate the control of potential future pandemics.
Keywords: Omicron variant; SARS-CoV-2; neutralization escape; neutralizing antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cross-Neutralization of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern by Antibodies Targeting Distinct Epitopes on Spike.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0297521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02975-21. Epub 2021 Nov 16. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34781736 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants.Elife. 2020 Oct 28;9:e61312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61312. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33112236 Free PMC article.
-
A Combination of Receptor-Binding Domain and N-Terminal Domain Neutralizing Antibodies Limits the Generation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Neutralization-Escape Mutants.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0247321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02473-21. Epub 2021 Oct 5. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34607456 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and antigenic variations in the spike protein of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Feb 17;18(2):e1010260. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010260. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35176090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Immunology of SARS-CoV-2.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jan;329(1):e13431. doi: 10.1111/imr.13431. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39731211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and function of an unusual R452-dependent monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0184424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01844-24. Epub 2025 Apr 8. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40197058 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental Effects of Anti-Nucleocapsid Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Reinfection, and the Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19.Pathogens. 2024 Dec 15;13(12):1109. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121109. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of neutralizing antibodies against COVID-19 Omicron subvariants following breakthrough infection in southwest China between December 2022 and April 2024.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jul 30;10(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02319-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40738879 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Genetic Insights, Epidemiological Tracking, and Implications for Vaccine Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1263. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031263. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes CO, Jette CA, Abernathy ME, Dam K-MA, Esswein SR, Gristick HB, Malyutin AG, Sharaf NG, Huey-Tubman KE, Lee YE, Robbiani DF, Nussenzweig MC, West AP Jr, Bjorkman PJ. 2020. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies. Nature New Biol 588:682–687. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2852-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes CO, West AP Jr, Huey-Tubman KE, Hoffmann MAG, Sharaf NG, Hoffman PR, Koranda N, Gristick HB, Gaebler C, Muecksch F, Lorenzi JCC, Finkin S, Hägglöf T, Hurley A, Millard KG, Weisblum Y, Schmidt F, Hatziioannou T, Bieniasz PD, Caskey M, Robbiani DF, Nussenzweig MC, Bjorkman PJ. 2020. Structures of human antibodies bound to SARS-CoV-2 spike reveal common epitopes and recurrent features of antibodies. Cell 182:828–842. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brouwer PJM, Caniels TG, van der Straten K, Snitselaar JL, Aldon Y, Bangaru S, Torres JL, Okba NMA, Claireaux M, Kerster G, et al. . 2020. Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability. Science 369:643–650. doi:10.1126/science.abc5902 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chi X, Yan R, Zhang J, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Hao M, Zhang Z, Fan P, Dong Y, Yang Y, Chen Z, Guo Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Song X, Chen Y, Xia L, Fu L, Hou L, Xu J, Yu C, Li J, Zhou Q, Chen W. 2020. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 369:650–655. doi:10.1126/science.abc6952 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

