Genetically Engineered Liposwitch-Based Nanomaterials
- PMID: 39495202
- PMCID: PMC11632658
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c01388
Genetically Engineered Liposwitch-Based Nanomaterials
Abstract
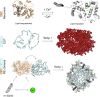
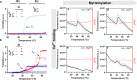
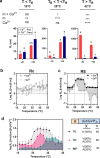
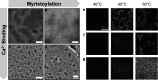
Fusion of intrinsically disordered and globular proteins is a powerful strategy to create functional nanomaterials. However, the immutable nature of genetic encoding restricts the dynamic adaptability of nanostructures postexpression. To address this, we envisioned using a myristoyl switch, a protein that combines allostery and post-translational modifications─two strategies that modify protein properties without altering their sequence─to regulate intrinsically disordered protein (IDP)-driven nanoassembly. A typical myristoyl switch, allosterically activated by a stimulus, reveals a sequestered lipid for membrane association. We hypothesize that this conditional exposure of lipids can regulate the assembly of fusion proteins, a concept we term "liposwitching". We tested this by fusing recoverin, a calcium-dependent myristoyl switch, with elastin-like polypeptide, a thermoresponsive model IDP. Biophysical analyses confirmed recoverin's myristoyl-switch functionality, while dynamic light scattering and cryo-transmission electron microscopy showed distinct calcium- and lipidation-dependent phase separation and assembly. This study highlights liposwitching as a viable strategy for controlling DP-driven nanoassembly, enabling applications in synthetic biology and cellular engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

