Prognostic Value of TGF-β Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39495544
- PMCID: PMC11562745
- DOI: 10.5152/tud.2024.24024
Prognostic Value of TGF-β Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a member of the growth factor superfamily that clinical studies address its association with bladder cancer invasion, progression, and metastasis. The present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to explore the prognostic significance of TGF-β expression in bladder cancer patients.
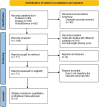
Materials and methods: The major international databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Scopus, were searched for full-text literature citations. The hazard ratio (HR) with a 95% CI as the effect size was applied as the appropriate summarized statistic. We used a random-effects model using the DerSimonian and Laird method to estimate the pooled effect size. To assess the heterogeneity among trials, the I-square (I 2 ) statistic and Cochran's Q test were used. Forest and funnel plots were drawn to respectively demonstrate the findings and detect any existing publication bias.
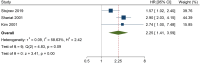
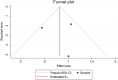
Results: This meta-analysis included 3 studies that met the criteria and included 535 patients. The combined HR for the selected studies was 2.250 (95% CI=(1.411, 3.586), P< .001) and no significant heterogeneity was detected between trials (I 2=58.63, P=.089). Furthermore, no severe asymmetry was seen within the funnel plot, indicating a lack of potential publication bias.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that TGF-β expression can remarkably predict a worse prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. The results of the present meta-analysis may be validated through further updated reviews and additional relevant investigations in future studies.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; TGF-β; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Sylvester RJ, Rodríguez O, Hernández V, et al. European Association of Urology (EAU) prognostic factor risk groups for non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) incorporating the WHO 2004/2016 and WHO 1973 classification systems for grade: an update from the EAU NMIBC Guidelines Panel. Eur Urol. 2021;79(4):480 488. ( 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.033) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous