A conserved juxtamembrane motif in plant NFR5 receptors is essential for root nodule symbiosis
- PMID: 39495923
- PMCID: PMC11572979
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2405671121
A conserved juxtamembrane motif in plant NFR5 receptors is essential for root nodule symbiosis
Abstract
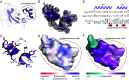
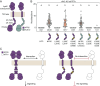
Establishment of root nodule symbiosis is initiated by the perception of bacterial Nod factor ligands by the plant LysM receptor kinases NFR1 and NFR5. Receptor signaling initiating the symbiotic pathway depends on the kinase activity of NFR1, while the signaling mechanism of the catalytically inactive NFR5 pseudokinase is unknown. Here, we present the crystal structure of the signaling-competent Lotus japonicus NFR5 intracellular domain, comprising the juxtamembrane region and pseudokinase domain. The juxtamembrane region is structurally well defined and forms two α-helices, αA and αA', which contain an exposed hydrophobic motif. We demonstrate that this "juxtamembrane motif" promotes NFR5-NFR5 and NFR1-NFR5 interactions and is essential for symbiotic signaling. Conservation analysis reveals that the juxtamembrane motif is present throughout NFR5-type receptors and is required for symbiosis signaling from barley RLK10, suggesting a conserved and broader function for this motif in plant-microbe symbioses.
Keywords: Nod factor receptors; kinases and pseudokinases; plant–microbe interactions; receptor signaling; root nodule symbiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Some findings from this article are considered for a patent application.
Figures


References
-
- Radutoiu S., et al. , Plant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases. Science 425, 585–592 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Madsen E. B., et al. , A receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legume perception of rhizobial signals. Science 425, 637–640 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Rübsam H., et al. , Nanobody-driven signaling reveals the core receptor complex in root nodule symbiosis. Science 379, 272–277 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

