Application of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol-etomidate mixture in radical gastrectomy under general anesthesia
- PMID: 39496064
- PMCID: PMC11537582
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039669
Application of dexmedetomidine combined with propofol-etomidate mixture in radical gastrectomy under general anesthesia
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer is the third most common malignant tumor with the second highest mortality rate in the world, and radical gastrectomy is the main treatment method, but the operation needs a long period of time to carry out and has strong surgical trauma stimulation, which is likely to cause sympathetic nerve excitement and stress reaction in the body. Therefore, the selection of appropriate anesthetic medication regimen and anesthesia method has an important impact on the intraoperative management and postoperative recovery of patients. This study aims to compare the clinical effects of dexmedetomidine alone in combination with propofol, etomidate and propofol-etomidate mixture in the treatment of radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
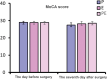
Methods: A total of 90 patients undergoing elective radical gastrectomy were randomly divided into the propofol group (group P), the etomidate group (group E), and the etomidate-propofol mixture group (group PE). Anesthesia induction was performed under the monitoring of bispectral index anesthesia depth. The same pumping drugs were used in 3 groups: 0.1 to 0.3 μg/kg·min remifentanil, 0.5 μg/kg·h dexmedetomidine, and 5 to 10 μg/kg·min rocuronium. The primary outcome indicator was the hemodynamic conditions. The secondary outcome indicators included awakening time and time to accurately answer questions after operation, the prevalence of postoperative respiratory depression and adverse events, the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction, and preoperative and postoperative Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-Mental State Examination scores.
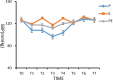
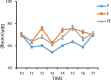
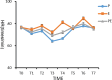
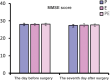
Results: Among the 3 groups of patients, the use rate of vasoactive drugs in group P was higher (P < .05); the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate of group P at T1 to T4 were significantly lower than those of groups E and PE (P < .05); the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate of group E in T2, T4, and T6 were significantly higher than those of groups P and PE (P < .05). The wake-up time after operation and the time to accurately answer the questions were longer in group E than in groups P and PE (P < .05). The incidence of postoperative respiratory depression in group P was higher than that in groups E and PE (P < .05). The Montreal Cognitive Assessment score of group P was lower than that of groups E and PE 7 days after operation (P < .05).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine combined with propofol-etomidate mixture is a better anesthesia drug combination.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Bai HX. Advances in the incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in China. Electronic J Clin Med Literature. 2019;6:192.
-
- Han C, Wu Q, Ni Z, et al. Correlation analysis between incidence of gastric cancer and statistical yearbook indicators in China from 1989 to 2014. J Canc Control Treat. 2019;32:434–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

