Self-Awareness from Whole-Body Movements
- PMID: 39496486
- PMCID: PMC11735670
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0478-24.2024
Self-Awareness from Whole-Body Movements
Abstract
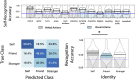
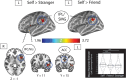
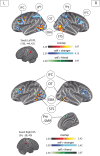
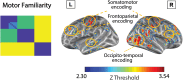
Humans can recognize their whole-body movements even when displayed as dynamic dot patterns. The sparse depiction of whole-body movements, coupled with a lack of visual experience watching ourselves in the world, has long implicated nonvisual mechanisms to self-action recognition. Using general linear modeling and multivariate analyses on human brain imaging data from male and female participants, we aimed to identify the neural systems for this ability. First, we found that cortical areas linked to motor processes, including frontoparietal and primary somatomotor cortices, exhibit greater engagement and functional connectivity when recognizing self-generated versus other-generated actions. Next, we show that these regions encode self-identity based on motor familiarity, even after regressing out idiosyncratic visual cues using multiple regression representational similarity analysis. Last, we found the reverse pattern for unfamiliar individuals: encoding localized to occipitotemporal visual regions. These findings suggest that self-awareness from actions emerges from the interplay of motor and visual processes.
Keywords: actions; motor; neuroimaging; self-awareness.
Copyright © 2024 the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Arbib MA (1981) Perceptual structures and distributed motor control. In: Handbook of physiology, section I: the nervous system, vol. 2: motor control (Brooks VB, ed.), pp 1449–1480. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
-
- Arbib MA (1992) Schema theory. In: The encyclopedia of artificial intelligence, Vol. 2, pp 1427–1443. New York, NY: Wiley Interscience.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
