PTPRK regulates glycolysis and de novo lipogenesis to promote hepatocyte metabolic reprogramming in obesity
- PMID: 39496584
- PMCID: PMC11535053
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53733-0
PTPRK regulates glycolysis and de novo lipogenesis to promote hepatocyte metabolic reprogramming in obesity
Abstract
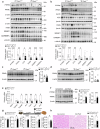
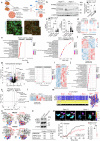
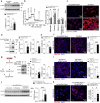
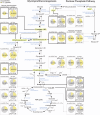
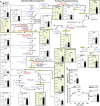
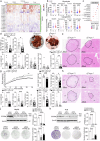
Fat accumulation, de novo lipogenesis, and glycolysis are key drivers of hepatocyte reprogramming and the consequent metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Here we report that obesity leads to dysregulated expression of hepatic protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs). PTPRK was found to be increased in steatotic hepatocytes in both humans and mice, and correlates positively with PPARγ-induced lipogenic signaling. High-fat-fed PTPRK knockout male and female mice have lower weight gain and reduced hepatic fat accumulation. Phosphoproteomic analysis in primary hepatocytes and hepatic metabolomics identified fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 and glycolysis as PTPRK targets in metabolic reprogramming. Mechanistically, PTPRK-induced glycolysis enhances PPARγ and lipogenesis in hepatocytes. Silencing PTPRK in liver cancer cell lines reduces colony-forming capacity and high-fat-fed PTPRK knockout mice exposed to a hepatic carcinogen develop smaller tumours. Our study defines the role of PTPRK in the regulation of hepatic glycolysis, lipid metabolism, and tumour development in obesity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.C.H. is a founder, director and shareholder in Stimuliver ApS and Stemnovate Limited. E.H.G., J.A.E. and E.N.G. are inventors of the patent “USES OF PROTEIN TYROSINE PHOSPHATASE RECEPTOR KAPPA INHIBITORS” submitted by the Université libre de Bruxelles and the Universidad Miguel Hernández de Elche (EP23382162.7, status pending). The manuscript demonstrates the interest of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor Kappa as drug target for the treatment of HCC and therefore provides background support for the development of inhibitors targeting this specific PTP. The patent application is itself however focused on such specific PTPRK inhibitors which are not disclosed in the manuscript. The pending patent application is disclosed even if no direct impact of the publication is expected on the value of the patent application. The remaining authors declare no competing interests. E.N.G. declares that there are no other relationships or activities that might bias, or be perceived to bias, the present work.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GA864921/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- PROMETEO/2021/059/Generalitat Valenciana (Regional Government of Valencia)
- GA817940/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

