Effects of SNP, MgSO4, and MgO-NPs foliar application on Spinacia oleracea L. growth and physio-biochemical responses under cadmium stress
- PMID: 39496661
- PMCID: PMC11535332
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77221-z
Effects of SNP, MgSO4, and MgO-NPs foliar application on Spinacia oleracea L. growth and physio-biochemical responses under cadmium stress
Abstract
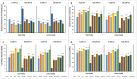
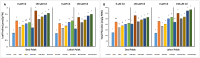
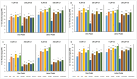
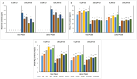
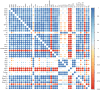
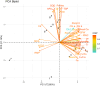
The effects of foliar application of sodium nitroprusside (SNP), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) and magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) on the growth, physiology, and gas exchange parameters of two varieties of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) under cadmium (Cd) stress were examined. The experiment was arranged in a completely randomized design with 72 pots. Two varieties of S. oleracea (Desi Palak & Lahori Palak) were used. Two concentrations of Cd (0 µM and 150 µM) in the form of cadmium chloride (CdCl2) were used. Two levels of SNP (0 ppm and 100 ppm) and two levels for each form of Mg i.e. MgSO4 and MgO-NPs (0 and 200 ppm) were foliar sprayed on plants in control and Cd stress. Both varieties behaved similarly under Cd stress and caused reductions in growth, physiology, gas exchange, water content parameters and inorganic ion uptake. However, the biochemical parameters like relative membrane permeability (RMP), malondialdehyde (MDA), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) contents were increased. However, all foliar spray treatments increased growth, physiological and gas exchange parameters, water content and inorganic ion uptake. However, this reduced the MDA, RMP, and H2O2 contents. Desi Palak showed the more positive results under foliar application of MgO-NPs. However, Lahori palak showed more positive results under the SNP + MgO-NP treatment. It is concluded that foliar application of SNP, MgSO4 and MgO-NPs could be an innovative approach to alleviated the heavy metals (Cd) toxicity in crop plants.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




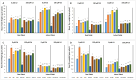
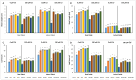
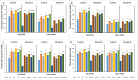

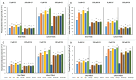



References
-
- Adegbeye, M. et al. Sustainable agriculture options for production, greenhouse gasses and pollution alleviation, and nutrient recycling in emerging and transitional nations-An overview. J. Clean. Prod.242, 118319 (2020). - DOI
-
- Waris, Z. et al. Efficacy of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on physio-biochemical attributes of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) under cadmium toxicity. J. Plant Growth Regul.42, 5041–5057 (2023). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

