Radiomics analysis in differentiating osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma based on T2-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging
- PMID: 39496777
- PMCID: PMC11535035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78245-1
Radiomics analysis in differentiating osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma based on T2-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging
Abstract
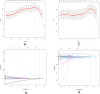
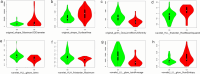
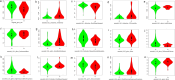
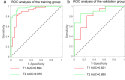
This study was performed to investigate the diagnostic value of radiomics models constructed by fat suppressed T2-weighted imaging (T2WI-FS) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (CET1) based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for differentiation of osteosarcoma (OS) and chondrosarcoma (CS). In this retrospective cohort study, we included all inpatients with pathologically confirmed OS or CS from Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (Hunan, China) as of October 2020. Demographic and imaging variables were extracted from electronic medical records and compared between OS and CS group. Totals of 530 radiomics features were extracted from CET1 and T2WI-FS sequences based on MRI. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method was used for screening and dimensionality reduction of the radiomics model. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to construct the radiomics model, and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was generated to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the radiomics model. The training cohort and validation cohort included 87 and 29 patients, respectively. 8 CET1 features and 15 T2WI-FS features were screened based on the radiomics features. In the training group, the area under the receiver-operator characteristic curve (AUC) value for CET1 and T2WI-FS sequences in the radiomics model was 0.894 (95% CI 0.817-0.970) and 0.970 (95% CI 0.940-0.999), respectively. In the validation group, the AUC value for CET1 and T2WI-FS sequences in the radiomics model was 0.821 (95% CI 0.642-1.000) and 0.899 (95% CI 0.785-1.000), respectively. In this study, we developed a radiomics model based on T2WI-FS and CET1 sequences to differentiate between OS and CS. This model exhibits good performance and can help clinicians make decisions and optimize the use of healthcare resources.
Keywords: Chondrosarcoma; Differential diagnosis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Osteosarcoma; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

