Clinical validation of an AI-based pathology tool for scoring of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
- PMID: 39496972
- PMCID: PMC11750710
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03301-2
Clinical validation of an AI-based pathology tool for scoring of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Abstract
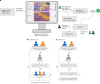
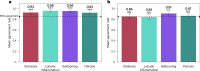
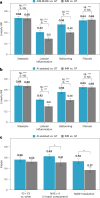
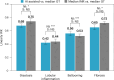
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality, yet treatment options are limited. Manual scoring of liver biopsies, currently the gold standard for clinical trial enrollment and endpoint assessment, suffers from high reader variability. This study represents the most comprehensive multisite analytical and clinical validation of an artificial intelligence (AI)-based pathology system, AI-based measurement of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (AIM-MASH), to assist pathologists in MASH trial histology scoring. AIM-MASH demonstrated high repeatability and reproducibility compared to manual scoring. AIM-MASH-assisted reads by expert MASH pathologists were superior to unassisted reads in accurately assessing inflammation, ballooning, MAS ≥ 4 with ≥1 in each score category and MASH resolution, while maintaining non-inferiority in steatosis and fibrosis assessment. These findings suggest that AIM-MASH could mitigate reader variability, providing a more reliable assessment of therapeutics in MASH clinical trials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H.P., H.H., A.S.-M., R.E., N.P., A.H.B. and N.P.A. are full-time, salaried employees of PathAI. K.E.W. was a full-time employee of PathAI during all phases of the study and is now a paid consultant of PathAI. S.A.H. is a paid consultant for Akero Therapeutics, Aligos Therapeutics, Altimmune, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bluejay Therapeutics, Echosens North America, Galecto, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Hepion Pharmaceuticals, Hepta Bio, HistoIndex, Kriya Therapeutics, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Medpace, MGGM Therapeutics, NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals, Northsea Therapeutics, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sagimet Biosciences, Terns and Viking Therapeutics and a shareholder of Akero, Cirius Therapeutics, Galectin Therapeutics, HistoIndex and Northsea Therapeutics. S.S.M., M.C.V., L.C.M., S.P.M.C., S.H.M., C.E.T. and M.C.M. were PathAI employees at the time of study conduct. J.G. and M.R. are paid contractors of PathAI. R.P.M. and G.M.S. are full-time, salaried employees of OrsoBio. C.C. is a full-time, salaried employee of Inipharm. S.D.P. is a full-time salaried employee of Gilead Sciences. A.-S.S. is a full-time, salaried employee of Novo Nordisk. A.M. was a paid consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb. V.B. is a full-time, salaried employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. A.J.S. has stock options in Genfit, Akarna, Tiziana, Indalo, Durect Inversago and Galmed; is a consultant to AstraZeneca, Nimbus, Takeda, Janssen, Gilead, Terns, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer and Genfit; and has been an unpaid consultant to Intercept, Echosens, Immuron, Galectin and Affimune Prosciento. His institution has received grant support from Gilead, Bristol Myers Squibb, Intercept, Merck, AstraZeneca and Novartis. He receives royalties from Elsevier and UptoDate. Q.M.A. is a coordinator of the EU IMI-2 LITMUS consortium, which is funded by the EU Horizon 2020 program and the EFPIA. This multistakeholder consortium includes industry partners. He has research grant funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Intercept. He is a consultant on behalf of Newcastle University to Alimentiv, Akero, AstraZeneca, 89bio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galmed, Genfit, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, HistoIndex, Intercept, Inventiva, QVIA, Janssen, Madrigal, Merck, NGM Bio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, PathAI, Pfizer, PharmaNest, Prosciento, Roche and Terns. He is a speaker for Novo Nordisk, Madrigal and Springer Healthcare and receives royalties from Elsevier. R.L. is a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Alnylam–Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bluejay Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals and Viking Therapeutics. He is a cofounder of LipoNexus. V.R. is a paid consultant for Novo Nordisk, Northsea Madrigal, Enyo, Poxel, Bristol Myers Squibb, Intercept, NGM Bio and Sagimet.
Figures
References
-
- FDA–NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, Endpoints, and other Tools) Resource (2016); https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK326791/ - PubMed

