Rab2A-mediated Golgi-lipid droplet interactions support very-low-density lipoprotein secretion in hepatocytes
- PMID: 39496977
- PMCID: PMC11649929
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00288-x
Rab2A-mediated Golgi-lipid droplet interactions support very-low-density lipoprotein secretion in hepatocytes
Abstract
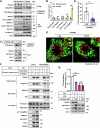
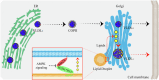
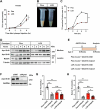
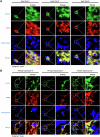
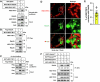
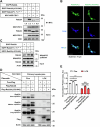
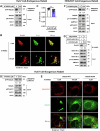
Lipid droplets (LDs) serve as crucial hubs for lipid trafficking and metabolic regulation through their numerous interactions with various organelles. While the interplay between LDs and the Golgi apparatus has been recognized, their roles and underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here, we reveal the role of Ras-related protein Rab-2A (Rab2A) in mediating LD-Golgi interactions, thereby contributing to very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) lipidation and secretion in hepatocytes. Mechanistically, our findings identify a selective interaction between Golgi-localized Rab2A and 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13 (HSD17B13) protein residing on LDs. This complex facilitates dynamic organelle communication between the Golgi apparatus and LDs, thus contributing to lipid transfer from LDs to the Golgi apparatus for VLDL2 lipidation and secretion. Attenuation of Rab2A activity via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) suppresses the Rab2A-HSD17B13 complex formation, impairing LD-Golgi interactions and subsequent VLDL secretion. Furthermore, genetic inhibition of Rab2A and HSD17B13 in the liver reduces the serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Collectively, this study provides a new perspective on the interactions between the Golgi apparatus and LDs.
Keywords: 17-Beta-hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 13; AMP-activated Protein Kinase; Organelle Interactions; Ras-related Protein Rab-2A; Very-low-density Lipoprotein.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adam M, Heikelä H, Sobolewski C, Portius D, Mäki-Jouppila J, Mehmood A, Adhikari P, Esposito I, Elo LL, Zhang F-P et al (2018) Hydroxysteroid (17β) dehydrogenase 13 deficiency triggers hepatic steatosis and inflammation in mice. FASEB J 32:3434–3447 - PubMed
-
- Barbosa AD, Savage DB, Siniossoglou S (2015) Lipid droplet-organelle interactions: emerging roles in lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Cell Biol 35:91–97 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82000549/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 32025019/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82470614/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2008085MC67/| Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province ()
- 0810013101/Doctoral Start-up Foundation of Anhui Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

