Serum triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in late pregnancy as a potential predictor of adverse birth outcomes: an analysis of real-world data
- PMID: 39497103
- PMCID: PMC11536801
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-024-01503-9
Serum triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in late pregnancy as a potential predictor of adverse birth outcomes: an analysis of real-world data
Abstract
Background: The association between serum triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (THR) in late pregnancy and adverse birth outcomes (ABO) remains controversial because of inconsistent results. The present study assessed the association between maternal serum THR and incidence of ABO [preterm birth (PTB), small and large for gestational age (SGA/LGA), low birth weight (LBW) and macrosomia] in a Chinese population.
Methods: A total of 11,553 consecutive participants from a real-world database with data on lipid profiles and birth outcomes were included. Logistic regression models were applied to assess the association between THR and incident ABO. Mediation analysis was performed to investigate the contribution of pregnancy complications [gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) and pre-eclampsia (PE)] to this association.
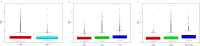
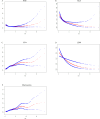
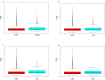
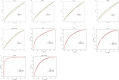
Results: Approximately 6.6% (762/11,553), 8.9% (1023/11,553), 15.5% (1792/11,553), 4.3% (494/11,553), and 7.4% (851/11,553) of individuals developed PTB, SGA, LGA, LBW and macrosomia, respectively. Significant trends across the quintiles of THR toward decreasing incidence of SGA and LBW and increasing incidence of LGA and macrosomia were observed. The multivariate-adjusted odds ratios (OR) in the top quintile of serum THR (> 3.16) versus the bottom quintile (< 1.44) were 0.52 for PTB, 0.48 for SGA, 0.64 for LBW, 2.80 for LGA and 3.80 for macrosomia, respectively. A 1-standard deviation (SD) increase in serum THR was associated with decreased risk of PTB [OR = 0.84, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.76-0.93), SGA (OR = 0.71, 95% CI:0.65-0.78) and LBW (OR = 0.76, 95% CI:0.65-0.90) and increased risk of LGA (OR = 1.40, 95% CI:1.32-1.49) and macrosomia (OR = 1.49, 95% CI:1.38-1.62). In mediation analyses, PE mediated - 19.8%, -10.6% and - 24.6% of THR-associated PTB, SGA and LBW, respectively, GDM accounted for - 3.7%, 6.8% and 4.3% of THR-associated PTB, LGA and macrosomia, respectively, and ICP explained - 1.9% and - 2.1% of THR-associated PTB and LBW, respectively. In addition, incorporating THR to ABO predictive models significantly improved the area under the curve for SGA (0.743 vs. 0.753, P < 0.001), LGA (0.734 vs. 0.745, P < 0.001) and macrosomia (0.786 vs. 0.800, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Real-world data showed an association between serum THR in late pregnancy and ABO risk, and this association may be partially mediated by prevalent pregnancy complications (PE/GDM/ICP), suggesting a potential role of THR in predicting ABO (SGA/LGA/macrosomia).
Keywords: Adverse birth outcome; Large for gestational age; Macrosomia; Preterm birth; Small for gestational age; Triglyceride/HDL–C ratio.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between maternal lipid profile and pregnancy complications and perinatal outcomes: a population-based study from China.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016 Mar 21;16:60. doi: 10.1186/s12884-016-0852-9. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016. PMID: 27000102 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal outcomes of singletons following vitrification versus slow-freezing of embryos: a multicenter cohort study using propensity score analysis.Hum Reprod. 2019 Sep 29;34(9):1788-1798. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez095. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31407797
-
Association of Maternal Serum Uric Acid and Cystatin C Levels in Late Pregnancy with Adverse Birth Outcomes: An Observational Cohort Study in China.Int J Womens Health. 2022 Feb 17;14:213-223. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S350847. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35210868 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the maternal birth status on offspring: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009;88(12):1307-18. doi: 10.3109/00016340903358820. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009. PMID: 19916879
-
The influence of embryo stage on obstetric complications and perinatal outcomes following programmed compared to natural frozen-thawed embryo transfer cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 16;14:1186068. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1186068. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37664838 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Global and regional incidence of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med. 2025 Feb 28;23(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-03935-0. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40022113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuan X, Gao Y, Zhang M, Long W, Liu J, Wang H, et al. Association of maternal D-dimer level in late pregnancy with birth outcomes in a Chinese cohort. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;501:258–63. - PubMed
-
- Ohuma EO, Moller AB, Bradley E, Chakwera S, Hussain-Alkhateeb L, Lewin A, et al. National, regional, and global estimates of preterm birth in 2020, with trends from 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2023;402(10409):1261–71. - PubMed
-
- Hazel EA, Erchick DJ, Katz J, Lee ACC, Diaz M, Wu LSF et al. Neonatal mortality risk of vulnerable newborns by fine stratum of gestational age and birthweight for 230 679 live births in nine low- and middle-income countries, 2000–2017. BJOG. 2024 Jan 16. - PubMed
-
- Ashorn P, Ashorn U, Muthiani Y, Aboubaker S, Askari S, Bahl R, UNICEF–WHO Low Birthweight Estimates Group, et al. Small vulnerable newborns-big potential for impact. Lancet. 2023;401(10389):1692–706. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekaran N. Induction of labor for a suspected large-for-gestational-age/macrosomic fetus. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2021;77:110–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

