Critical role of ROCK1 in AD pathogenesis via controlling lysosomal biogenesis and acidification
- PMID: 39497162
- PMCID: PMC11533276
- DOI: 10.1186/s40035-024-00442-9
Critical role of ROCK1 in AD pathogenesis via controlling lysosomal biogenesis and acidification
Abstract
Background: Lysosomal homeostasis and functions are essential for the survival of neural cells. Impaired lysosomal biogenesis and acidification in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis leads to proteolytic dysfunction and neurodegeneration. However, the key regulatory factors and mechanisms of lysosomal homeostasis in AD remain poorly understood.
Methods: ROCK1 expression and its co-localization with LAMP1 and SQSTM1/p62 were detected in post-mortem brains of healthy controls and AD patients. Lysosome-related fluorescence probe staining, transmission electron microscopy and immunoblotting were performed to evaluate the role of ROCK1 in lysosomal biogenesis and acidification in various neural cell types. The interaction between ROCK1 and TFEB was confirmed by surface plasmon resonance and in situ proximity ligation assay (PLA). Moreover, we performed AAV-mediated ROCK1 downregulation followed by immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and behavioral tests to unveil the effects of the ROCK1-TFEB axis on lysosomes in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
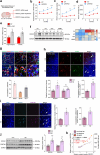
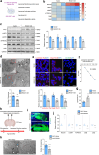
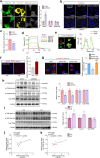
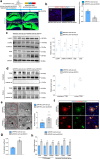
Results: ROCK1 level was significantly increased in the brains of AD individuals, and was positively correlated with lysosomal markers and Aβ. Lysosomal proteolysis was largely impaired by the high abundance of ROCK1, while ROCK1 knockdown mitigated the lysosomal dysfunction in neurons and microglia. Moreover, we verified ROCK1 as a previously unknown upstream kinase of TFEB independent of m-TOR or GSK-3β. ROCK1 elevation resulted in abundant extracellular Aβ deposition which in turn bound to Aβ receptors and activated RhoA/ROCK1, thus forming a vicious circle of AD pathogenesis. Genetically downregulating ROCK1 lowered its interference with TFEB, promoted TFEB nuclear distribution, lysosomal biogenesis and lysosome-mediated Aβ clearance, and eventually prevented pathological traits and cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice.
Conclusion: In summary, our results provide a mechanistic insight into the critical role of ROCK1 in lysosomal regulation and Aβ clearance in AD by acting as a novel upstream serine kinase of TFEB.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Lysosomal acidification; Lysosomal biogenesis; ROCK1; TFEB.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Lawrence RE, Zoncu R. The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(2):133–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

