Distinct neuroinflammatory patterns between cerebral microbleeds and microinfarcts in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- PMID: 39497506
- PMCID: PMC11651216
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.52226
Distinct neuroinflammatory patterns between cerebral microbleeds and microinfarcts in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Abstract
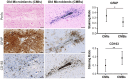
In this neuropathological study, we investigated neuroinflammation surrounding recent and old cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) and cerebral microinfarcts (CMIs) in 18 cases of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). We used several serial stainings and immunolabellings to identify microvascular lesions, define their recent or old stage, and characterize neuroinflammatory response (scavenging activity and astrogliosis). We found that both CMBs and CMIs induce a neuroinflammatory response, which was more pronounced in old lesion than recent. Astrogliosis and scavenging activity were differentially prominent according to the ischemic/hemorrhagic nature of the lesion. Our findings provide insights into the pathophysiology of microvascular injuries in CAA.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
R.B., M.P., M.P., V.D., and V.B.: None. L.P. declares the following type of interests: speaker fees (Novonordisk). C.C. declares the following type of interests: speaker fees (Bristol‐Myers Squibb); international RCT Steering committees for Biogen and Bayer.
Figures

References
-
- Puy L, Rauch A, Deramecourt V, Cordonnier C, Bérézowski V. Acute microbleeds and microinfarcts within the perihematomal area after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2023;54:e58‐e62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
