Influence of budesonide and fluticasone propionate in the anti-osteoporotic potential in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via stimulation of osteogenic differentiation
- PMID: 39497989
- PMCID: PMC11532851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39475
Influence of budesonide and fluticasone propionate in the anti-osteoporotic potential in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via stimulation of osteogenic differentiation
Abstract
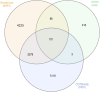
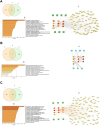
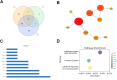
Osteoporosis is a prevalent bone condition with adverse effects observed in patients undergoing long-term glucocorticoid therapy, resulting in bone demineralization and tissue loss. There has been limited studies on the global response to dexamethasone in terms of comparing its expression profile to other common glucocorticoids during osteogenic differentiation. This study focused on the downregulated gene expression profile of glucocorticoid compounds; dexamethasone, budesonide, and fluticasone propionate, during osteogenic differentiation to elucidate the related target genes and pathways associated with the anti-osteoporotic potential of telomerase-immortalized human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells using a bioinformatics approach. Based on gene expression microarrays experiments and bioinformatics analysis, several key genes involved in the regulation of osteogenic differentiation and osteoporosis development in mesenchymal stem cells that were targeted by these specific glucocorticoids were determined. Network analysis using GeneCards, OMIM, and CTD databases were performed and osteoporosis-related genes were identified. LIMMA and moderated Welch test R packages were performed to determine significant downregulated differentially expressed genes for each glucocorticoid treatment. A total of 479 (dexamethasone), 84 (budesonide), and 889 (fluticasone propionate) differentially expressed genes were identified for each glucocorticoid, of which 35 common genes overlapped. Enrichment pathway analysis was conducted using Metascape, and protein-protein interaction networks were constructed using the STRING database and Cytoscape software to determine potential target genes involved with osteoporosis. Enrichment pathway analysis revealed genes involved in 3 Reactome pathways namely cytokine signaling in immune system, immune system and the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathways and identified 10 hub genes based on the PPI network to determine potential target pathways associated with osteoporosis. These findings provide preliminary insights into the relationship between the key target genes of dexamethasone, budesonide, and fluticasone propionate, and the pathways associated with regulated osteoporosis metabolism during osteogenic differentiation.
Keywords: Anti-Osteoporosis; Bioinformatics approach; Glucocorticoid compound; Mesenchymal stem cells; Osteogenic differentiation.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
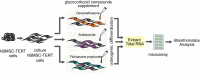



References
-
- Yuasa M., Yamada T., Taniyama T., Masaoka T., Xuetao W., Yoshii T., Horie M., Yasuda H., Uemura T., Okawa A., Sotome S. Dexamethasone enhances osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow- and muscle-derived stromal cells and augments ectopic bone formation induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2. PLoS One. 2015;10(2) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116462. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shalhoub V., Conlon D., Tassinari M., Quinn C., Partridge N., Stein G.S., Lian J.B. Glucocorticoids promote development of the osteoblast phenotype by selectively modulating expression of cell growth and differentiation associated genes. J. Cell. Biochem. 1992;50(4):425–440. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500411. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

