Ship recycling process in Bangladesh and a survey-based risk assessment with mitigation proposal
- PMID: 39497999
- PMCID: PMC11532836
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39344
Ship recycling process in Bangladesh and a survey-based risk assessment with mitigation proposal
Abstract
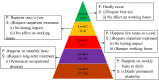
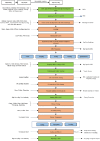
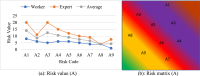
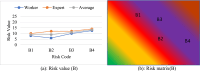
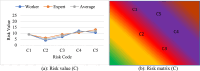
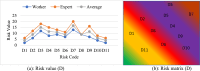
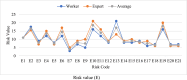
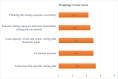
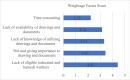
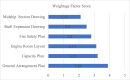
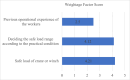
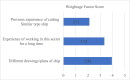
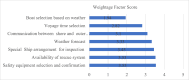
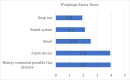
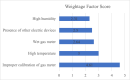
Ship recycling industries play a significant role in the economic development of South Asian countries, including Bangladesh. In the wake of entering the Hong Kong Convention (HKC) in June 2025, the industry aims to improve its overall safety standards cost-effectively. However, due to the restrictive nature of the industry, solutions based on field surveys are limited. This study successfully articulates the indigenous industry knowledge of the recycling process in Bangladesh after carefully studying the practices followed by the existing ship recycling yards in the country. Based on field surveys conducted across 18 ship recycling yards in Bangladesh, the risk patterns inherent in the ship recycling industry are studied; for example, highly hazardous tasks in the ship recycling process are found to be (i) explosion hazards during primary cutting operations at the intertidal zone, (ii) falling hazards during inspections at the outer anchorage, (iii) falling and crushing hazards during block cutting and handling heavy objects. Industry experts and scholars consider the perception of the risk pattern regarding the current practices of ship recycling activities to cover a broader perspective of this issue. The correlation of survey outcomes with actual accident cases is comparable. Finally, practical recommendations for minimising risks have been recommended, especially in high-risk workplace areas. The study adds knowledge to the existing literature by giving a clear picture of evidence-based findings for this sector and helps improve the industry's overall safety standard.
Keywords: Field surveys; High-risk workplace; Risk patterns; Ship recycling.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This research is funded by Engineering X, an international collaboration founded by the 10.13039/501100000287Royal Academy of Engineering and 10.13039/100008885Lloyd's Register Foundation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of health risks associated with potentially toxic element contamination of soil by end-of-life ship dismantling in Bangladesh.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Aug;26(23):24162-24175. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05608-x. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31228056
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ship breaking area and associated ecological risk assessment: evidence from the Sitakund ship-breaking area in Bangladesh.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Aug;31(39):51733-51746. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34569-z. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39126587
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the future mesothelioma disease burden from past exposure to asbestos in ship recycling yards in India.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020 Apr;225:113478. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113478. Epub 2020 Feb 9. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 32050148
-
Environmental hazards associated with open-beach breaking of end-of-life ships: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Nov;25(31):30880-30893. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3159-8. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30215211 Review.
References
-
- UNCTAD UNCTAD handbook of statistics 2022. 2022. https://unctad.org/meeting/launch-handbook-statistics-2022
-
- Solakivi T., Kiiski T., Kuusinen T., Ojala L. The European Ship Recycling Regulation and its market implications: ship-recycling capacity and market potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;294
-
- Garmer K., Sjöström H., Hiremath A.M., Tilwankar A.K., Kinigalakis G., Asolekar S.R. Development and validation of three-step risk assessment method for ship recycling sector. Saf. Sci. 2015;76:175–189.
-
- Choi J.K., Kelley D., Murphy S., Thangamani D. Economic and environmental perspectives of end-of-life ship management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016;107:82–91.
-
- Zakaria N.G., Ali M.T., Hossain K.A. Underlying problems of ship recycling industries in Bangladesh and way forward. J. Nav. Architect. Mar. Eng. 2012;9(2):91–102.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

