Hsa_circ_0004194 suppresses colorectal cancer progression via hsa-miR-27a-3p
- PMID: 39498085
- PMCID: PMC11532888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39549
Hsa_circ_0004194 suppresses colorectal cancer progression via hsa-miR-27a-3p
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the functional role and the underlying molecular mechanisms associated with hsa_circ_0004194 in the context of colorectal cancer (CRC) and to elucidate its impact on cancer progression.
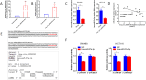
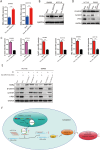
Results: A notable and statistically significant decrease in the expression levels of hsa_circ_0004194 was observed specifically within CRC tissues when compared to non-tumor colorectal mucosa tissues. Functional evaluations, such as CCK8 assays, plate clone formation analysis, and transwell migration assays, our study revealed hsa_circ_0004194 significantly reduced the activity behavior of CRC cells. This overexpression of hsa_circ_0004194 effectively hindered these key cellular processes, demonstrating its role in suppressing the aggressive behaviors of CRC cells. Additionally, in vivo experiments utilizing mouse xenograft models exhibited that the upregulation of hsa_circ_0004194 significantly attenuated tumor growth, reduced tumor volume, and diminished liver metastasis. Further mechanistic investigation, through the utilization of RNA pull-down and luciferase reporter assays, uncovered that hsa_circ_0004194 sequestered hsa-miR-27a-3p, thereby enhancing retinoic acid X receptor α (RXRα)' expression which is in CRC cells. Moreover, this circular RNA also impeded the signaling pathway of Wnt/β-catenin.
Conclusion: Our study is the first to demonstrate that hsa_circ_0004194 exhibits downregulated expression in CRC and functions as a ceRNA by binding to and sequestering hsa-miR-27a-3p, thereby modulating the RXRα/β-catenin signaling pathway to inhibit CRC progression. This discovery suggests that hsa_circ_0004194 holds significant potential as a therapeutic biomarker for patients with CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Hsa-miR-27a-3p; RXRα; hsa_circ_0004194.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F., Laversanne M., Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024 May-Jun;74(3):229–263. - PubMed
-
- Chen X., Zhou M., Yant L., Huang C. Circular RNA in disease: basic properties and biomedical relevance. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Nov;13(6) - PubMed
-
- Jian X., He H., Zhu J., Zhang Q., Zheng Z., Liang X., Chen L., Yang M., Peng K., Zhang Z., Liu T., Ye Y., Jiao H., Wang S., Zhou W., Ding Y., Li T. Hsa_circ_001680 affects the proliferation and migration of CRC and mediates its chemoresistance by regulating BMI1 through miR-340. Mol. Cancer. 2020 Jan 31;19(1):20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen S., Li K., Guo J., Chen H.N., Ming Y., Jin Y., Xu F., Zhang T., Yang Y., Ye Z., Liu W., Ma H., Cheng J., Zhou J.K., Li Z., Shen S., Dai L., Zhou Z.G., Xu H., Peng Y. circNEIL3 inhibits tumor metastasis through recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4L to degrade YBX1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 28;120(13) - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

