Comparison and chemometrics analysis of phenolic compounds and mineral elements in Artemisia Argyi Folium from different geographical origins
- PMID: 39498249
- PMCID: PMC11533654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101909
Comparison and chemometrics analysis of phenolic compounds and mineral elements in Artemisia Argyi Folium from different geographical origins
Abstract
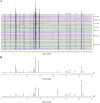
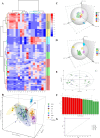
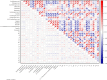
The quality of Artemisia Argyi Folium (AAF), a traditional Chinese food ingredient, is intrinsically linked to its geographical origin, which this study explores through phenolic compounds and mineral elements. The contents of 17 phenols and 18 minerals differed significantly between geographically distinct samples according to UHPLC and ICP-MS, respectively. Chemometrics indicated that a supervised model, orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), outperformed unsupervised methods at classifying AAF samples by their origins. Phenols were more effective at distinguishing samples from seven provinces, while minerals were adept at differentiating samples from the Dabie Mountain region (three provinces) and those from four other provinces. Six phenols and 10 minerals were important variables for discrimination. Complex correlations were observed between the contents of various phenols and minerals in AAF, with minerals possibly affecting the accumulation of phenols. This study provides an approach for distinguishing geographically distinct AAF samples and determining their geographical origins.
Keywords: Artemisia Argyi Folium; Chemometrics; Geographical origin; Mineral elements; Phenolic compounds.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Multi-omics approach combining GC-MS, LC-MS, and FT-NIR with chemometrics and machine learning for metabolites systematic profiling and geographical origin tracing of Artemisia argyi Folium.J Chromatogr A. 2025 Aug 30;1757:466138. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2025.466138. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Chromatogr A. 2025. PMID: 40527046
-
[Comparison on volatile components between Artemisiae Verlotori Folium and Artemisiae Argyi Folium based on GC-MS and chemometrics].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Dec;48(23):6334-6346. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230901.101. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38211990 Chinese.
-
[Content of mineral elements in different Artemisia argyi germplasms and their relationship with quality properties].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Feb;47(4):880-888. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211108.101. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35285186 Chinese.
-
A review of the research progress on Artemisia argyi Folium: botany, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, and clinical application.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7473-7500. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03122-7. Epub 2024 May 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38775853 Review.
-
Rapid identification of traditional Chinese medicines (Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos) and their origins using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 Feb 15;307:123639. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2023.123639. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024. PMID: 37979539 Review.
Cited by
-
Artemisia and the Elements: A Botanical Symphony of Minerals and Metals.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jun 20. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04706-x. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40540239 Review.
References
-
- Chang Y.Q., Fan W.X., Shi H., Feng X., Zhang D., Wang L.…Guo L. Characterization of phenolics and discovery of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Artemisia argyi leaves based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and relevance analysis. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2022;220 doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114982. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Commission, C. P. I. China Medical Science Press; Beijing: 2020. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

