Risk Factors for Multidrug Resistance in Patients Infected with Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Nomogram
- PMID: 39498412
- PMCID: PMC11534326
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S479374
Risk Factors for Multidrug Resistance in Patients Infected with Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Nomogram
Abstract
Purpose: Our aim was to determine the risk factors for multidrug resistance in patients with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP).
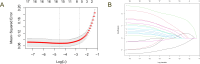
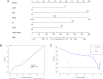
Methods: The information of 196 patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae infection was collected. The patients were subsequently assigned to the carbapenem-resistant, multidrug-resistant, and non-multidrug-resistant groups. The risk factors for multidrug resistance in CRKP patients were assessed via least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and logistic regression analyses. Moreover, a nomogram was constructed dependent on the identified risk factors, and calibration and decision curves were plotted to detect its accuracy.
Results: Length of stay (LOS) [odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI): 4.558 (1.157-17.961), P = 0.030], intensive care unit (ICU) stay within 30 days [OR and 95% CI: 12.643 (3.780-42.293), P < 0.001], Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score [OR and 95% CI: 13.569 (2.738-67.236), P = 0.001], fungal infection [OR and 95% CI: 6.398 (1.969-20.785), P = 0.002], and cardiovascular disease (CVD) [OR and 95% CI: 3.871 (1.293-11.592), P = 0.016] were identified as risk factors for multidrug resistance in CRKP patients. The concordance index (C-index) of the constructed nomogram was 0.950 (95% CI: 0.945-0.955). Moreover, decision curve analysis elucidated the nomogram utilization across a wide range of probability thresholds, ranging from 1% to 100%. Finally, internal validation using random data validated the robustness of the predictive model, yielding a C-index of 0.937.
Conclusion: The LOS, ICU stay within 30 days, GCS score, fungal infection, and CVD were recognized as risk factors for multidrug resistance in CRKP patients. The constructed nomogram could accurately predict multidrug-resistant CRKP infections in patients.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; carbapenem; multidrug resistance; prediction model; risk factors.
Plain language summary
The LOS, ICU stay within 30 days, GCS, fungal infection, and CVD were identified as risk factors for multidrug resistance in CRKP patients.The nomogram constructed in this study had high predictive accuracy.This study provides a reference for the formulation of personalized prevention and therapy strategies.
© 2024 Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Risk Factors for Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection and Construction of Nomogram Model: A Large Case-Control and Cohort Study from Shanxi, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Nov 29;16:7351-7363. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S442909. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38050629 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Predictive Nomogram for Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Children in a Grade 3 First-Class General Hospital in Central China.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jan 5;17:41-49. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S437742. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38197067 Free PMC article.
-
Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Aug 24;18(1):20230774. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0774. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37663230 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare-associated carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections are associated with higher mortality compared to carbapenem-susceptible K. pneumoniae infections in the intensive care unit: a retrospective cohort study.J Hosp Infect. 2024 Jun;148:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2024.03.003. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Hosp Infect. 2024. PMID: 38513959
-
Risk factors for carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection relative to two types of control patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020 Jan 31;9(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-0686-0. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020. PMID: 32005246 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical Characteristics, Virulence Profile, and Molecular Epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 6;18:1303-1311. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S506794. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40065763 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical prediction model to distinguish between colonization and infection by Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 23;15:1508030. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1508030. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39917270 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

