Latitudinal patterns in ocean C:N:P reflect phytoplankton acclimation and macromolecular composition
- PMID: 39499637
- PMCID: PMC11572967
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2404460121
Latitudinal patterns in ocean C:N:P reflect phytoplankton acclimation and macromolecular composition
Abstract
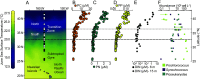
The proportions of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in surface ocean particulate matter deviate greatly from the canonical Redfield Ratio (C:N:P = 106:16:1) in space and time with significant implications for global carbon storage as this matter reaches the deep ocean. Recent work has revealed clear latitudinal patterns in C:N:P, yet the relative importance of ecological, physiological, or biochemical processes in creating these patterns is unclear. We present high-resolution, concurrent measurements of particulate C:N:P, macromolecular composition, environmental conditions, and plankton community composition from a transect spanning a subtropical-subpolar boundary, the North Pacific Transition Zone. We find that the summed contribution of macromolecules to particulate C, N, and P is consistent with, and provides interpretation for, particulate C:N:P patterns. A decline in particulate C:N from the subtropical to subpolar North Pacific largely reflects an increase in the relative contribution of protein compared to carbohydrate and lipid, whereas variation in C:P and N:P correspond to shifts in protein relative to polyphosphate, DNA, and RNA. Possible causes for the corresponding trends in C:N and macromolecular composition include physiological responses and changes in community structure of phytoplankton, which represented approximately 1/3rd of particulate C across the transect. Comparison with culture experiments and an allocation-based model of phytoplankton macromolecular composition suggest that physiological acclimation to changing nutrient supply is the most likely explanation for the latitudinal trend in C:N, offering both a mechanistic interpretation and biochemical basis for large-scale patterns in C:N:P.
Keywords: acclimation; elemental stoichiometry; nutrients; phytoplankton.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Volk T., Hoffert M. I., “Ocean carbon pumps: Analysis of relative strengths and efficiencies in ocean-driven atmospheric CO2 changes” in The Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO: Natural Variations Archean to Present, Sundquist E. T., Broecker W. S., Eds. (American Geophysical Union, 1985), pp. 99–110.
-
- Redfield A. C., The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 46, 205–221 (1958). - PubMed
-
- Weber T. S., Deutsch C., Ocean nutrient ratios governed by plankton biogeography. Nature 467, 550 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Martiny A. C., Vrugt J. A., Primeau F. W., Lomas M. W., Regional variation in the particulate organic carbon to nitrogen ratio in the surface ocean. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 27, 723–731 (2013).
-
- Martiny A. C., et al. , Strong latitudinal patterns in the elemental ratios of marine plankton and organic matter. Nat. Geosci. 6, 279–283 (2013).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

