Factors regulating the gripping force and stiffness of 25- and 27-gauge internal limiting membrane forceps
- PMID: 39499714
- PMCID: PMC11537382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310419
Factors regulating the gripping force and stiffness of 25- and 27-gauge internal limiting membrane forceps
Abstract
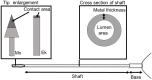
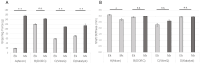
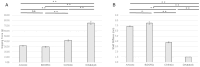
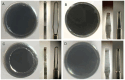
This study aimed to identify the factors affecting the gripping force and stiffness of 25-gauge and 27-gauge (25G and 27G, respectively) internal limiting membrane (ILM) forceps and to compare the effect of these factors on various ILM forceps manufactured by different companies. This study evaluated 25G and 27G ILM forceps with two different types of tip shapes, Eckardt and Maxgrip, manufactured by Alcon (A), DORC (B), VitreQ (C), and Katalyst (D). The gripping force was defined as the force required to move the ILM forceps away from a thin paper by pulling the paper. Shaft stiffness was determined by measuring the shaft displacement under a known force. Multiple regression analysis revealed that the gripping force showed significant correlations with the gauge (P<0.001), type of shaft tip (Eckardt/Maxgrip) (P<0.001), and contact area of the tip (P<0.001). The shaft stiffness showed significant correlations with the gauge (P<0.001), length of the base (P<0.001), thickness of the metal of the shaft (P = 0.05), and lumen area of the shaft (P = 0.01). The gripping force and shaft stiffness differed for each product. Thus, vitreoretinal surgeons must select the appropriate type of ILM forceps based on their characteristics.
Copyright: © 2024 Katakami et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: [One of authors, Hisanori Imai, have a research grant from Alcon Japan(IIT#64918391)].
Figures







References
-
- O’Malley C, Heintz RM Sr. Vitrectomy with an alternative instrument system. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975;7: 585–588, 591–594. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

