Clinical outcomes of early-stage triple-negative breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to HER2-low status☆
- PMID: 39500139
- PMCID: PMC11570474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103973
Clinical outcomes of early-stage triple-negative breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to HER2-low status☆
Abstract
Background: The impact of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) on outcomes in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (eTNBC) is unclear. Using a large, multi-institutional cohort, we evaluated outcomes by HER2 IHC status in patients with eTNBC who received neoadjuvant therapy (NAT).
Patients and methods: Patients with stage I-III TNBC who received NAT and underwent surgery from January 2016 to June 2019 were identified from three databases. HER2 expression was defined as low (IHC1+ or 2+/FISH not amplified) or HER2 IHC score 0 by local testing at diagnosis. Pathological complete response (pCR) rates were compared using logistic regression adjusted for multiple factors. Survival outcomes were estimated using Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards models.
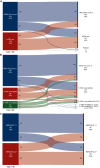
Results: Among 977 consecutive patients, 388 (39.7%) had HER2-low and 589 (60.3%) had HER2 IHC score 0 tumors. Median age at eTNBC diagnosis was 50.3 years (range 21.0-83.4 years). At baseline, clinical nodal positivity rate was significantly higher in HER2-low (55.0%) versus HER2 IHC score 0 tumors (46.6%) (P = 0.011); pCR rates were similar (32.0% versus 32.6%; adjusted P = 0.924). At a median follow-up of 3.5 years, recurrence-free survival (RFS) did not vary significantly between HER2-low versus HER2 IHC score 0 among patients with pCR (adjusted P = 0.368) or residual disease (RD) after NAT (adjusted P = 0.573). Distant RFS and overall survival (OS) did not differ by HER2 category for patients with pCR [distant RFS (DRFS), adjusted P = 0.509; OS, adjusted P = 0.514] or RD (DRFS, adjusted P = 0.812; OS, P = 0.285). Discordance of tumor HER2 status was seen in 31.1% of HER2 IHC score 0 cases, with HER2 expression observed post-treatment; 34.8% of HER2-low cases showed discordance, with absent HER2 expression in RD.
Conclusions: In this large cohort of patients with eTNBC treated with NAT, HER2-low status was not associated with pCR or survival after adjusting for clinical factors. The discordance in HER2 IHC pre- and post-NAT likely reflects challenges in HER2 quantification and heterogeneity.
Keywords: HER2 low; TNBC; breast cancer; early stage; pCR; survival.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wolff A.C., Hammond M.E.H., Schwartz J.N., et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131(1):18–43. - PubMed
-
- Wolff A.C., Somerfield M.R., Dowsett M., et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology–College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023;147(9):993–1000. - PubMed
-
- Tarantino P., Hamilton E., Tolaney S.M., et al. HER2-low breast cancer: pathological and clinical landscape. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(17):1951–1962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

