The biochemical mechanisms of plastic biodegradation
- PMID: 39500541
- PMCID: PMC11644497
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuae027
The biochemical mechanisms of plastic biodegradation
Abstract
Since the invention of the first synthetic plastic, an estimated 12 billion metric tons of plastics have been manufactured, 70% of which was produced in the last 20 years. Plastic waste is placing new selective pressures on humans and the organisms we depend on, yet it also places new pressures on microorganisms as they compete to exploit this new and growing source of carbon. The limited efficacy of traditional recycling methods on plastic waste, which can leach into the environment at low purity and concentration, indicates the utility of this evolving metabolic activity. This review will categorize and discuss the probable metabolic routes for each industrially relevant plastic, rank the most effective biodegraders for each plastic by harmonizing and reinterpreting prior literature, and explain the experimental techniques most often used in plastic biodegradation research, thus providing a comprehensive resource for researchers investigating and engineering plastic biodegradation.
Keywords: biodegradation; bioremediation; engineering; metabolic; metabolism; plastic.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
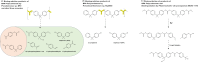
Figures



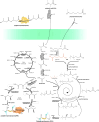
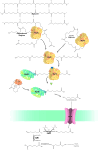


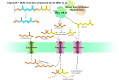
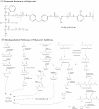

Similar articles
-
Current advances, challenges and strategies for enhancing the biodegradation of plastic waste.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jan 1;906:167850. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167850. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 37844647 Review.
-
New perspectives in plastic biodegradation.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011 Jun;22(3):422-6. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.01.013. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21356588
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of plastic waste biodegradation.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2005 Oct-Dec;25(4):243-50. doi: 10.1080/07388550500346359. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16419620 Review.
-
[Microbial degradation of polyurethane plastics].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018 Sep 25;34(9):1398-1409. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170532. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 30255674 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Ackermann YS, Li W-J, Op de Hipt L et al. Engineering adipic acid metabolism in Pseudomonas putida. Metab Eng. 2021;67:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Ágnes N, Rajmund K. The environmental impact of plastic waste incineration. AARMS—Acad Appl Res Mil Public Manag Sci. 2016;15:231–7.
-
- Akutsu-Shigeno Y, Adachi Y, Yamada C et al. Isolation of a bacterium that degrades urethane compounds and characterization of its urethane hydrolase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;70:422–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

