The Neuroprotection of 1,2,4-Triazole Derivative by Inhibiting Inflammation and Protecting BBB Integrity in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 39500736
- PMCID: PMC11537802
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70113
The Neuroprotection of 1,2,4-Triazole Derivative by Inhibiting Inflammation and Protecting BBB Integrity in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
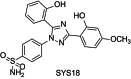
Background: The oxidative stress and neuroinflammation are important factors in acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Our former study showed the 1,2,4- triazole derivative (SYS18) had obviously neuroprotection by anti- oxidative stress on rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model.
Aim: In this study, we continue to investigate its neuroprotection by anti-inflammatory effects and protecting BBB integrity in AIS.
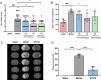
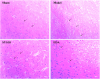
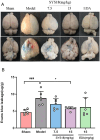
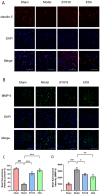
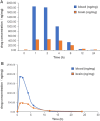
Methods and results: First, its effect on acute inflammation was evaluated by the mice model of increased peritoneal capillary permeability. Then, the MCAO cerebral edema models were built to evaluate its neuroprotection by reducing the neurological score, cerebral edema, improving the biochemical indicators, and pathological damage of brain tissue. At the same time, its protection on blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity was proved by decreasing the BBB permeability and inhibiting glycocalyx degradation and regulating the BBB tight junction proteins expression of matrix metalloproteinase- 9 (MMP- 9) and claudin- 5 in brain tissue. Meanwhile, pharmacokinetic experiments showed that the compound had good BBB penetration. It has some advantages in the intensity of efficacy compared with the marketed drug edaravone.
Conclusion: Based on these findings, SYS18 has a strong potential to become a neuroprotectant in the future.
Keywords: 1,3,5‐triphenyl‐1,2,4‐triazole derivative; blood–brain barrier; glycocalyx; inflammatory.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tirzepatide mitigates Stroke-Induced Blood-Brain barrier disruption by modulating Claudin-1 and C/EBP-α pathways.Mol Med. 2025 Jul 23;31(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01312-4. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40702450 Free PMC article.
-
Rosmarinic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier dysfunction to improve cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 15;1003:177882. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177882. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40609608
-
The Protective Effect of Low-dose Nicotine on Ischemia Stroke by Maintaining the Integrity of the Blood-Brain Barrier.Nicotine Tob Res. 2025 Jul 22;27(8):1420-1429. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntaf034. Nicotine Tob Res. 2025. PMID: 39921606
-
Sulfonylurea drugs for people with severe hemispheric ischemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 11;3(3):CD014802. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014802.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40066941
-
The Effects of Cannabinoids on Ischemic Stroke-Associated Neuroinflammation: A Systematic Review.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 3;20(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10171-z. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39899062 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ligustrazine Alleviates Blood-Brain Barrier Damage by Downregulating Expression of miR-297c-5p.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 May;31(5):e70367. doi: 10.1111/cns.70367. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40406932 Free PMC article.
-
The glycocalyx: a key target for treatment of severe acute pancreatitis-associated multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.Hum Cell. 2025 May 24;38(4):107. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01227-6. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40411704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caloric Restriction Preserves BBB Integrity After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia Through Reducing Neutrophil Infiltration.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70257. doi: 10.1111/cns.70257. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39915908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu H., Qiu K., He Q., Lei Q., and Lu W., “Mechanisms of Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Herpes Simplex Encephalitis,” Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology 14, no. 2 (2019): 157–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

