OTUB1 regulation of ferroptosis and the protective role of ferrostatin-1 in lupus nephritis
- PMID: 39500879
- PMCID: PMC11538433
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07185-5
OTUB1 regulation of ferroptosis and the protective role of ferrostatin-1 in lupus nephritis
Abstract
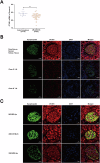
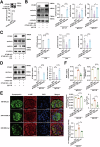
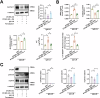
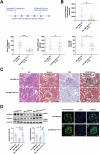
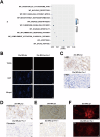
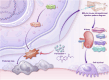
Lupus nephritis (LN) is a prevalent and severe manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), leading to significant morbidity and mortality. OTUB1, a deubiquitinating enzyme, has emerged as a potential therapeutic target due to its role in cellular protection and regulation of ferroptosis, a form of cell death linked to LN. Our study revealed significantly reduced OTUB1 expression in the glomeruli of LN patients and podocytes, correlated with disease severity. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated OTUB1 knockout in podocytes resulted in pronounced injury, indicated by decreased levels of nephrin and podocin. Ferrostatin-1 treatment effectively mitigated this injury, restoring SLC7A11 expression and significantly reducing MDA levels, Fe2+ levels, BODIPY C11 expression, and normalized cysteine and glutathione expression. In the MRL/lpr mouse model, Ferrostatin-1 significantly improved renal function decreased proteinuria, and ameliorated renal histopathological changes, including reduced glomerular endothelial swelling, mesangial cell proliferation, and leukocyte infiltration. These results underscore the protective role of Ferrostatin-1 in modulating the pathogenesis of LN. OTUB1 plays a crucial protective role against podocyte injury in LN by regulating ferroptosis. Ferrostatin-1 effectively mitigates podocyte damage induced by OTUB1 deficiency, suggesting that targeting ferroptosis could be a promising therapeutic strategy for LN.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

