Antimicrobial susceptibility of enterobacterales causing bloodstream infection in United States medical centres: comparison of aztreonam-avibactam with beta-lactams active against carbapenem-resistant enterobacterales
- PMID: 39501203
- PMCID: PMC11536805
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-10133-5
Antimicrobial susceptibility of enterobacterales causing bloodstream infection in United States medical centres: comparison of aztreonam-avibactam with beta-lactams active against carbapenem-resistant enterobacterales
Abstract
Background: Bloodstream infection (BSI) is associated with poor outcomes especially when effective antimicrobial therapy and control of infection source are delayed. As the frequency of Enterobacterales producing metallo-β-lactamases (MBL) and/or OXA-48-like carbapenemases is increasing in some United States (US) medical centres, effective antimicrobials to treat the infections caused by these organisms are urgently needed. Aztreonam-avibactam is under clinical development for treatment of infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, including MBL producers.
Objectives: To evaluate the antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacterales causing BSI in US medical centres and compare the activity of aztreonam-avibactam with ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, imipenem-relebactam, cefiderocol, and other antimicrobials used to treat BSI.
Methods: 4,802 Enterobacterales were consecutively collected (1/patient) from 72 US medical centres in 2020-2022 and susceptibility tested by broth microdilution. Aztreonam-avibactam was tested with avibactam at a fixed concentration of 4 mg/L. A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic susceptible breakpoint of ≤ 8 mg/L was applied for aztreonam-avibactam for comparison. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) isolates were tested for β-lactamase-encoding genes using Next-generation sequencing.
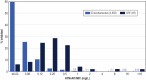
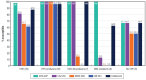
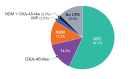
Results: Aztreonam-avibactam was highly active against Enterobacterales; only 2 isolates showed aztreonam-avibactam MICs > 8 mg/L: 1 meropenem-susceptible E. coli and 1 K. aerogenes (CRE). All carbapenemase producers and 98.0% of CRE were inhibited at an aztreonam-avibactam MIC of ≤ 8 mg/L. CRE susceptibility rates were 81.6% for ceftazidime-avibactam, 65.3% for meropenem-vaborbactam, 61.2% for imipenem-relebactam, and 87.8% for cefiderocol. Aztreonam-avibactam retained activity (MIC, ≤ 8 mg/L) against all (100.0%) meropenem-vaborbactam nonsusceptible (n = 17), 99.5% of imipenem-relebactam nonsusceptible (n = 206), and 90.0% of ceftazidime-avibactam nonsusceptible (n = 10) isolates. The most common carbapenemases were KPC-2/3 (57.1% of CREs), OXA-48-like (16.3%), and NDM (14.3%). A carbapenemase gene was not observed in 12.3% of CREs. Ceftazidime-avibactam and meropenem-vaborbactam were active against 100.0% of KPC producers, but ceftazidime-avibactam showed limited activity against MBL producers and meropenem-vaborbactam showed limited activity against OXA-48-like and MBL producers. The most active non-β-lactam comparators against CRE were gentamicin (49.0% susceptible) and amikacin (44.9% susceptible).
Conclusions: Aztreonam-avibactam demonstrated potent activity against a large collection of Enterobacterales isolated from patients with BSI in US hospitals, including CRE, MBL producers, and isolates resistant to recently approved β-lactamase inhibitor combinations.
Keywords: Bacteraemia; Bloodstream infection; Cefiderocol; Ceftazidime-avibactam; Enterobacterales; MBL.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adrie C, Garrouste-Orgeas M, Ibn Essaied W, Schwebel C, Darmon M, Mourvillier B, et al. Attributable mortality of ICU-acquired bloodstream infections: impact of the source, causative micro-organism, resistance profile and antimicrobial therapy. J Infect. 2017;74(2):131–41. - PubMed
-
- Sader HS, Mendes RE, Carvalhaes CG, Kimbrough JH, Castanheira M. Changing epidemiology of carbapenemases among carbapenem-resistant enterobacterales from United States hospitals and the activity of aztreonam-avibactam against contemporary Enterobacterales (2019–2021). Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(2):ofad046. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

