Application of the online teaching model based on BOPPPS virtual simulation platform in preventive medicine undergraduate experiment
- PMID: 39501207
- PMCID: PMC11536896
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-06175-7
Application of the online teaching model based on BOPPPS virtual simulation platform in preventive medicine undergraduate experiment
Abstract
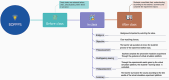
Background: As online teaching gains prevalence in higher education, traditional face-to-face methods are encountering limitations in meeting the demands of medical ethics, the availability of experimental resources, and essential experimental conditions. Consequently, under the guidance of the BOPPPS (bridge-in, objective, preassessment, participatory learning, postassessment, summary) teaching model, the application of virtual simulation platform has become a new trend. The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of BOPPPS combined with virtual simulation experimental teaching on students' scores and the evaluation of students' participation, performance and teachers' self-efficacy in preventive medicine experiment.
Methods: Students from Class 1 and Class 2 of 2019 preventive medicine major in Binzhou Medical University were selected as the research objects. The experimental group (class 2) (n = 51) received the teaching mode combined with BOPPPS and virtual simulation platform, while the control group (class 1) (n = 49) received the traditional experimental teaching method. After class, the experimental report scores, virtual simulation scores, students' engagement scale (SES), Biggs questionnaires, and teachers' sense of self-efficacy (TSES) questionnaires were analyzed.
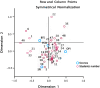
Results: The experimental report results demonstrated a significant increase in the total score of the experimental group and the scores of each of the four individual experiments compared to the control group (P < 0.05). To investigate the impact of the new teaching model on students' learning attitudes and patterns, as well as to evaluate teachers' self-efficacy, a questionnaire survey was administered following the course. The SES results showed that students in the experimental group had high performance scores on the two dimensions of learning methods and learning emotions (t = 2.476, t = 2.177; P = 0.015, P = 0.032). Furthermore, in the Biggs questionnaire, the total deep learning score of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (t = 2.553, P = 0.012), and the deep learning motivation score of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (t = 2.598, P = 0.011). The TSES questionnaire shows that most teachers think it is easier to manage students and the classroom and easier to implement teaching strategies under this mode.
Conclusions: The combination of BOPPPS and the virtual simulation platform effectively enhances the experimental environment for students, thereby improving their academic performance, engagement and learning approach in preventive medicine laboratory courses.
Keywords: BOPPPS model; Experimental teaching evaluation; Experimental teaching implementation; Preventive medicine; Virtual simulation platform.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the BOPPPS model on otolaryngologic education for five-year undergraduates.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Aug 9;24(1):860. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05868-3. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39123159 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of blended learning with BOPPPS model on Chinese medical undergraduate students: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of 44 studies.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Aug 23;24(1):914. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05917-x. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39180016 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the impact of virtual simulation experiment and massive open online course (MOOC) on medical students' wound debridement training: a quasi-experimental study.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Sep 18;24(1):1023. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05991-1. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39294595 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the application of CBL combined with BOPPPS teaching mode in oral and maxillofacial surgery teaching: a randomized controlled study.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 3;14(1):26510. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77432-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39489751 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Application effect of BOPPPS teaching model on fundamentals of nursing education: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 May 9;11:1319711. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1319711. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38784229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of research feedback experimental teaching mode for medical undergraduate students and comparative study with traditional experimental teaching mode.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):961. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07538-4. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40597174 Free PMC article.
-
Does a virtual simulation teaching platform improve surgical training for medical undergraduate students?BMC Surg. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12893-025-03029-x. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 40611031 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ji J, Liu N, Kou RR, Li SX, Li SB, Ma SF, Hu M, Tian G, Zhao XL. Application and research of virtual simulation technology in experimental teaching of preventive medicine. Prev Med Tribune. 2019;25(06):417–20.
-
- Zhang T, Fang ZM, Hu MY, Chen Y, Gao Y. Application of mixed teaching model in preventive medicine experimental teaching. Sci Wenhui. 2023;19(17):107–10.
-
- Wang F, Wei JP, Zhang YX, He R, Yuan YH,Yue TL. Exploration of blended teaching based on virtual simulation platform -- taking cognitive practice as an example. Food Ind. 2024;45(07):248–51.
-
- Yao ZJ, Dong Y. Research on virtual simulation experiment design and teaching innovation of public health emergency management. Guangdong Vocat Tech Educ Res. 2023;14(05):134–7.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials