Welcome to the operating theatre! Introductory bootcamp in operating theatre specialities for medical students
- PMID: 39501215
- PMCID: PMC11539667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-06165-9
Welcome to the operating theatre! Introductory bootcamp in operating theatre specialities for medical students
Abstract
Introduction: Since the early 2000's, the appeal of certain operating room specialties has decreasedamong medical school graduate students. The recent reform of the second and third cycles of medical studies in France provides an opportunity to set up teaching programs around operating room specialties. We have organised a teaching unit which is part of the final year of medical studies. The main objectives are: (1) to examine whether a boot camp can modify students' opinions and preconceived assumptions about a surgical and/or anaesthetist career (2) to determine whether these changes in perception, have an impact on students' interest in pursuing a surgical/anaesthetic career compared with the current situation.
Materials and methods: The "working in the operating theatre" boot camp (UETB) took place after the written exams of the sixth year of medical school, before students choose their future specialty for residency. This program included practical workshops, readings and time for exchanges surgeons and anaesthetists. At the beginning and at the end of the UETB, feedback forms were collected.
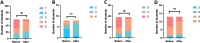
Results: The cohort included 59 students from the Toulouse medical school, academic year 2023-2024. After attending the UETB, there was a significant qualitative improvement in interest in a surgical and intensive care-anaesthesia career. Feedback on how the UETB influenced the choice of a future specialty was very positive, with statistically significant qualitive improvement., Additionally, the students' perception of a work-life quality as a surgeon and/or anaesthetist improved significantly.
Conclusion: The outcome of this study makes a strong case for integrating additional exposure to the various surgical subspecialties into the graduate medical curriculum in France. By helping to dispel misperceptions of "a surgical/anaesthetist career" early on, opportunities such as the UETB program may enable addressing the attrition rate observed among surgical and anaesthetic residency applications.
Keywords: Anaesthesia Education; Career; Medical Students; Stereotype; Surgical Education; Undergraduate Medical Education.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
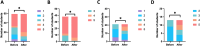
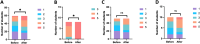
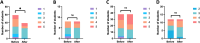
References
-
- Azizzadeh A, McCollum CH, Miller CC, Holliday KM, Shilstone HC, Lucci A. Factors influencing career choice among medical students interested in surgery. Curr Surg. 2003;60:210–3. - PubMed
-
- Lefèvre JH, Karila L, Kerneis S, Rouprêt M. Motivation of French medical students to pursue surgical careers: results of national survey of 1742 students. J Visc Surg. 2010;147:e181-186. - PubMed
-
- Maggiori L, Brouquet A, Zeitoun JD, Roupret M, Lefevre J-H. The future of gastrointestinal surgery in France: national survey of 929 medical students and results of professional choices after the 2008 national ranking exam. J Chir (Paris). 2009;146:168–74. - PubMed
-
- Cochran A, Paukert JL, Neumayer LA. Does a general surgery clerkship influence student perceptions of surgeons and surgical careers? Surgery. 2003;134:153–7. - PubMed
-
- Gawad N, Moussa F, Christakis GT, Rutka JT. Planting the “SEAD”: early comprehensive exposure to surgery for medical students. J Surg Educ. 2013;70:487–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

