Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Implementation Leadership Scale in the context of nurses
- PMID: 39501377
- PMCID: PMC11539699
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11721-6
Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Implementation Leadership Scale in the context of nurses
Abstract
Background: The implementation of evidence-based practices (EBPs) in healthcare is of critical importance, and nursing leadership plays a significant role in this process; however, there is a lack of validated instruments to measure the effectiveness of implementation leadership for EBPs. This study aims to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Implementation Leadership Scale (ILS) within the context of nursing.
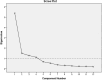
Methods: Data were obtained through a cross-sectional study. The original ILS was first translated into Turkish and then back into English. The scale was administered to 343 nurses working in a training and research hospital in Türkiye. Content validity was assessed with input from 10 experts. The data set was randomly divided into two subsamples to evaluate the construct validity of the ILS. Exploratory factor analyse (EFA) was conducted in sub-sample 1 (n = 172) and Confirmatory factor analyse (CFA) was conducted in sub-sample 2 (n = 171). Reliability was assessed using Cronbach's alpha values, test-retest reliability, item-total statistics, and split-half reliability.
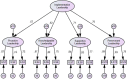
Results: The content validity index was calculated to be 0.96, indicating high validity. EFA revealed that the scale consists of four factors with eigenvalues greater than 1, and these factors together explained a high proportion of the total variance (77.10%). Confirmatory factor analysis results (χ2 / df = 1.29; CFI = 0.98; GFI = 0.94; AGFI = 0.91; NFI = 0.94; RMSEA = 0.04) confirmed that the Turkish version of the ILS maintains the original four-factor structure (Proactive, Knowledgeable, Supportive, and Perseverant leadership). Cronbach's alpha values (0.80-0.88) and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) (0.78-0.86) were found to be high. Item-total correlations (0.38-0.63) and the Spearman-Brown coefficient (0.75) were above acceptable levels.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that the Turkish version of the ILS is a valid and reliable tool for assessing implementation leadership in evidence-based practice (EBP) among nurses. This version of the ILS could contribute to further research on implementation leadership in Türkiye, international comparisons of EBP leadership, and the development of EBP practices.
Keywords: Evidence-based practice; Implementation leadership; Nurses; Reliability; Türkiye; Validity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and Validity of the Japanese Version of the Implementation Leadership Scale for Nurse Managers and Staff Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Nurs Manag. 2023 Oct 23;2023:4080434. doi: 10.1155/2023/4080434. eCollection 2023. J Nurs Manag. 2023. PMID: 40225600 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the health belief model scale for colorectal cancer screening.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 22;25(1):1887. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23127-y. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40405162 Free PMC article.
-
Validity and reliability of the Greek version of Implementation Leadership Scale (ILS).BMC Psychol. 2020 May 14;8(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s40359-020-00413-5. BMC Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32410660 Free PMC article.
-
Turkish validity and reliability study of the adolescent asthma self-efficacy questionnaire.J Pediatr Nurs. 2024 Jul-Aug;77:e450-e457. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2024.05.009. Epub 2024 May 10. J Pediatr Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38729897 Review.
-
Measuring Health Care Work-Related Contextual Factors: Development of the McGill Context Tool.J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2024 Winter 01;44(1):18-27. doi: 10.1097/CEH.0000000000000514. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2024. PMID: 37341570 Review.
References
-
- Zhang YP, Liu WH, Yan YT, Porr C, Zhang Y, Wei HH. Psychometric testing of the evidence-based practice nursing Leadership Scale and the Work Environment Scale after Cross-cultural Adaptation in Mainland China. Eval Heal Prof. 2019;42:328–43. 10.1177/0163278718801439. - PubMed
-
- Saiki M, Tomotaki A, Fukahori H, Yamamoto T, Nishigaki M, Matsuoka C et al. Reliability and Validity of the Japanese Version of the Implementation Leadership Scale for Nurse Managers and Staff Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Nurs Manag. 2023;2023. 10.1155/2023/4080434.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous