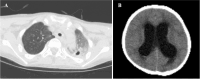
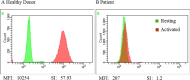
Two distinct clinical progressions of P67phox-deficient CGD, both commencing with cervical lymphadenitis
- PMID: 39501406
- PMCID: PMC11539424
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01813-8
Two distinct clinical progressions of P67phox-deficient CGD, both commencing with cervical lymphadenitis
Abstract
We present two rare cases of p67phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) caused by compound heterozygous mutations in the NCF2 gene. They developed cervical lymphadenitis as the initial manifestation of CGD but had distinct clinical progressions. Patient 1 presented with aspergillous meningitis, an extremely rare manifestation of neurological involvement in CGD, which has not been reported before. Patient 2 presented with non-infectious inflammatory lymphadenitis is also very rare and has not been reported previously. These cases emphasize the importance of considering p67phox-deficient CGD in children with late-onset invasive fungal infections and non-infectious inflammatory lesions. Additionally, we also reviewed previous reports of Chinese patients with P67phox-Deficient CGD. Our objective is to raise awareness about the clinical, diagnostic, and genetic characteristics of P67phox-deficient CGD in China, to reduce misdiagnosis and improve the management and prognosis of the disease.
Keywords: Chinese; Chronic granulomatous disease; NCF2 gene; Phenotype; Variant.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel NCF2 Mutation Causing Chronic Granulomatous Disease.J Clin Immunol. 2020 Oct;40(7):977-986. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00820-8. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32666379
-
Chronic Granulomatous Disease Due to Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor (NCF2) Gene Mutations in Three Unrelated Families.J Clin Immunol. 2017 Feb;37(2):109-112. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0366-2. Epub 2016 Dec 29. J Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28035544
-
A Founder Effect of c.257 + 2T > C Mutation in NCF2 Gene Underlies Severe Chronic Granulomatous Disease in Eleven Patients.J Clin Immunol. 2016 Aug;36(6):547-54. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0299-9. Epub 2016 May 25. J Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27220316
-
A novel variant in the neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) gene results in severe disseminated BCG infectious disease: A clinical report and literature review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Jun;8(6):e1237. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1237. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32281309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic granulomatous disease: a 25-year patient registry based on a multistep diagnostic procedure, from the referral center for primary immunodeficiencies in Greece.J Clin Immunol. 2013 Nov;33(8):1302-9. doi: 10.1007/s10875-013-9940-z. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24081483 Review.
References
-
- Yu HH, Yang YH, Chiang BL. Chronic granulomatous disease: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(2):101–13. 10.1007/s12016-020-08800-x. - PubMed
-
- Roos D, van Leeuwen K, Hsu AP, Priel DL, Begtrup A, Brandon R, Rawat A, Vignesh P, Madkaikar M, Stasia MJ, Bakri FG, de Boer M, Roesler J, Köker N, Köker MY, Jakobsen M, Bustamante J, Garcia-Morato MB, Shephard JLV, Cagdas D, Tezcan I, Sherkat R, Mortaz E, Fayezi A, Shahrooei M, Wolach B, Blancas-Galicia L, Kanegane H, Kawai T, Condino-Neto A, Vihinen M, Zerbe CS, Holland SM, Malech HL, Gallin JI, Kuhns DB. Hematologically important mutations: the autosomal forms of chronic granulomatous disease (third update). Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2021;92:102596. 10.1016/j.bcmd.2021.102596. Epub 2021 Jul 28. - PubMed
-
- Roos D. Chronic granulomatous disease. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1982:531–42. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9424-3_32. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Wang WF, Zhang YD, Chen TX. Clinical features and genetic analysis of 48 patients with chronic granulomatous disease in a single center study from Shanghai, China (2005–2015): new studies and a literature review. J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8745254. 10.1155/2017/8745254. Epub 2017 Jan 30. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ozturk B, Incesu L, Camlidag I. Chronic granulomatosis disease with meningitis and multiple brain abscesses. Pediatr Neurol. 2014;51(4):589–90. 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.06.014. Epub 2014 Jun 28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources