CUL3-related neurodevelopmental disorder: Clinical phenotype of 20 new individuals and identification of a potential phenotype-associated episignature
- PMID: 39501558
- PMCID: PMC11617854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100380
CUL3-related neurodevelopmental disorder: Clinical phenotype of 20 new individuals and identification of a potential phenotype-associated episignature
Abstract
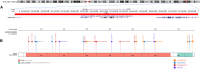
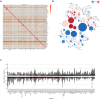
Neurodevelopmental disorder with or without autism or seizures (NEDAUS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delay, speech delay, seizures, autistic features, and/or behavior abnormalities. It is caused by CUL3 (Cullin-3 ubiquitin ligase) haploinsufficiency. We collected clinical and molecular data from 26 individuals carrying pathogenic variants and variants of uncertain significance (VUS) in the CUL3 gene, including 20 previously unreported cases. By comparing their DNA methylation (DNAm) classifiers with those of healthy controls and other neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by established episignatures, we aimed to create a diagnostic biomarker (episignature) and gain more knowledge of the molecular pathophysiology. We discovered a sensitive and specific DNAm episignature for patients with pathogenic variants in CUL3 and utilized it to reclassify patients carrying a VUS in the CUL3 gene. Comparative epigenomic analysis revealed similarities between NEDAUS and several other rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorders with previously identified episignatures, highlighting the broader implication of our findings. In addition, we performed genotype-phenotype correlation studies to explain the variety in clinical presentation between the cases. We discovered a highly accurate DNAm episignature serving as a robust diagnostic biomarker for NEDAUS. Furthermore, we broadened the phenotypic spectrum by identifying 20 new individuals and confirming five previously reported cases of NEDAUS.
Keywords: CUL3; DNA methylation; NEDAUS; episignature; genotype-phenotype correlation; intellectual disability.
Crown Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests B.S. is a shareholder in EpiSign Inc., a biotech firm involved in the commercial application of EpiSign technology.
Figures


References
-
- da Silva Montenegro E.M., Costa C.S., Campos G., Scliar M., de Almeida T.F., Zachi E.C., Silva I.M.W., Chan A.J.S., Zarrei M., Lourenço N.C.V., et al. Meta-Analyses Support Previous and Novel Autism Candidate Genes: Outcomes of an Unexplored Brazilian Cohort. Autism Res. 2020;13:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Iwafuchi S., Kikuchi A., Endo W., Inui T., Aihara Y., Satou K., Kaname T., Kure S. A novel stop-gain CUL3 mutation in a Japanese patient with autism spectrum disorder. Brain Dev. 2021;43:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima M., Kato M., Matsukura M., Kira R., Ngu L.H., Lichtenbelt K.D., van Gassen K.L.I., Mitsuhashi S., Saitsu H., Matsumoto N. De novo variants in CUL3 are associated with global developmental delays with or without infantile spasms. J. Hum. Genet. 2020;65:727–734. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

