Landscape of respiratory syncytial virus
- PMID: 39501814
- PMCID: PMC11706595
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003354
Landscape of respiratory syncytial virus
Abstract
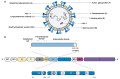
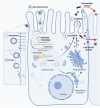
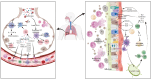
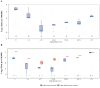
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the Orthopneumovirus genus of the Pneumoviridae family in the order Mononegavirales. RSV can cause acute upper and lower respiratory tract infections, sometimes with extrapulmonary complications. The disease burden of RSV infection is enormous, mainly affecting infants and older adults aged 75 years or above. Currently, treatment options for RSV are largely supportive. Prevention strategies remain a critical focus, with efforts centered on vaccine development and the use of prophylactic monoclonal antibodies. To date, three RSV vaccines have been approved for active immunization among individuals aged 60 years and above. For children who are not eligible for these vaccines, passive immunization is recommended. A newly approved prophylactic monoclonal antibody, Nirsevimab, which offers enhanced neutralizing activity and an extended half-life, provides exceptional protection for high-risk infants and young children. This review provides a comprehensive and detailed exploration of RSV's virology, immunology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Copyright © 2024 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What U.S. Obstetricians Need to Know About Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Mar 1;143(3):e54-e62. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005492. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38061043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nirsevimab Immunization to Prevent Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Infants and Children up to 24 Months of Age.Nurs Womens Health. 2024 Feb;28(1):75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.nwh.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Nurs Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38070539
-
New Approaches to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prevention and Treatment.Annu Rev Med. 2025 Jan;76(1):13-28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-061323-073934. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Annu Rev Med. 2025. PMID: 39656962 Review.
-
Early Estimate of Nirsevimab Effectiveness for Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Hospitalization Among Infants Entering Their First Respiratory Syncytial Virus Season - New Vaccine Surveillance Network, October 2023-February 2024.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024 Mar 7;73(9):209-214. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7309a4. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024. PMID: 38457312 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults.BMJ. 2019 Sep 10;366:l5021. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5021. BMJ. 2019. PMID: 31506273 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of bacterial co-detection in respiratory syncytial virus-positive children in Wenzhou, China, 2021 to 2023.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 May 14;25(1):697. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11086-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40369488 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus D3189 modulates antiviral and inflammatory responses in primary nasal epithelial cells, reducing respiratory syncytial virus shedding.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 8;15:1625517. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1625517. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40697815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bénet T Sánchez Picot V Messaoudi M Chou M Eap T Wang J, et al. . Microorganisms associated with pneumonia in children <5 years of age in developing and emerging countries: The GABRIEL pneumonia multicenter, prospective, case-control study. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:604–612. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix378. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Langedijk AC, Bont LJ. Respiratory syncytial virus infection and novel interventions. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023;21:734–749. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00919-w. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

