Advanced Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Gold, Silver, and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Oncological Applications
- PMID: 39501968
- PMCID: PMC11804848
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202403059
Advanced Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Gold, Silver, and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Oncological Applications
Abstract
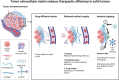
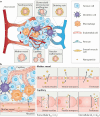
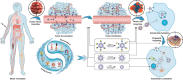
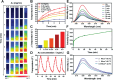
Cancer remains one of the most challenging health issues globally, demanding innovative therapeutic approaches for effective treatment. Nanoparticles, particularly those composed of gold, silver, and iron oxide, have emerged as promising candidates for changing cancer therapy. This comprehensive review demonstrates the landscape of nanoparticle-based oncological interventions, focusing on the remarkable advancements and therapeutic potentials of gold, silver, and iron oxide nanoparticles. Gold nanoparticles have garnered significant attention for their exceptional biocompatibility, tunable surface chemistry, and distinctive optical properties, rendering them ideal candidates for various cancer diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Silver nanoparticles, renowned for their antimicrobial properties, exhibit remarkable potential in cancer therapy through multiple mechanisms, including apoptosis induction, angiogenesis inhibition, and drug delivery enhancement. With their magnetic properties and biocompatibility, iron oxide nanoparticles offer unique cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy opportunities. This review critically examines the recent advancements in the synthesis, functionalization, and biomedical applications of these nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Moreover, the challenges are discussed, including toxicity concerns, immunogenicity, and translational barriers, and ongoing efforts to overcome these hurdles are highlighted. Finally, insights into the future directions of nanoparticle-based cancer therapy and regulatory considerations, are provided aiming to accelerate the translation of these promising technologies from bench to bedside.
Keywords: cancer therapy; combination therapy; diagnostic; drug delivery; gold nanoparticles; imaging, iron oxide nanoparticles; metallic nanoparticles; personalized medicine; silver nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Recent advances in gold and silver nanoparticles: synthesis and applications.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014 Jul;14(7):4757-80. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.9526. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24757945 Review.
-
Gold, Silver and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Bionanoconjugation Strategies Aimed at Electrochemical Applications.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2020 Jan 7;378(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s41061-019-0275-y. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2020. PMID: 31907672 Review.
-
A review of small molecules and drug delivery applications using gold and iron nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Mar 11;14:1633-1657. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S184723. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30880970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal-based nanoparticles: Promising tools for the management of cardiovascular diseases.Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug;36:102433. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2021.102433. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34171467 Review.
-
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor-targeted therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;11(2):184-9. doi: 10.2174/156800911794328475. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21158723 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Ferroptosis-Immunotherapy Nanoplatforms: Multidimensional Engineering for Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling and Therapeutic Optimization.Nanomicro Lett. 2025 Sep 2;18(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s40820-025-01862-6. Nanomicro Lett. 2025. PMID: 40892295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Green Synthesis Route of ZnO Nanoparticles for Dielectric Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;15(13):991. doi: 10.3390/nano15130991. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648698 Free PMC article.
-
Folate-Modified Albumin-Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Theranostics: Engineering and In Vitro PDT Treatment of Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 30;17(8):982. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17080982. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40871005 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory nanoplatforms with multiple mechanisms of action in cancer treatment.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Jun;20(11):1321-1338. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2500906. Epub 2025 May 7. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40331271 Review.
-
Advances in nanocarrier-mediated cancer therapy: Progress in immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Aug 20;138(16):1927-1944. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003703. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40545573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilhelm S., Tavares A. J., Dai Q., Ohta S., Audet J., Dvorak H. F., Chan W. C. W., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16014.
-
- Entezari M., Yousef Abad G. G., Sedghi B., Ettehadi R., Asadi S., Beiranvand R., Haratian N., Karimian S. S., Jebali A., Khorrami R., Zandieh M. A., Saebfar H., Hushmandi K., Salimimoghadam S., Rashidi M., Taheriazam A., Hashemi M., Ertas Y. N., Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

