Synthetic injectable and porous hydrogels for the formation of skeletal muscle fibers: Novel perspectives for the acellular repair of substantial volumetric muscle loss
- PMID: 39502329
- PMCID: PMC11536390
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314241283148
Synthetic injectable and porous hydrogels for the formation of skeletal muscle fibers: Novel perspectives for the acellular repair of substantial volumetric muscle loss
Abstract
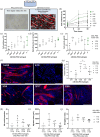
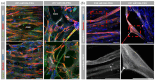
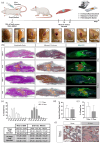
In severe skeletal muscle damage, muscle tissue regeneration process has to face the loss of resident muscle stem cells (MuSCs) and the lack of connective tissue necessary to guide the regeneration process. Biocompatible and standardized 3D structures that can be injected to the muscle injury site, conforming to the defect shape while actively guiding the repair process, holds great promise for skeletal muscle tissue regeneration. In this study, we explore the use of an injectable and porous lysine dendrimer/polyethylene glycol (DGL/PEG) hydrogel as an acellular support for skeletal muscle regeneration. We adjusted the DGL/PEG composition to achieve a stiffness conducive to the attachment and proliferation of murine immortalized myoblasts and human primary muscle stems cells, sustaining the formation and maturation of muscle fibers in vitro. We then evaluated the potential of one selected "myogenic-porous hydrogel" as a supportive structure for muscle repair in a large tibialis anterior muscle defect in rats. This injectable and porous formulation filled the defect, promoting rapid cellularization with the presence of endothelial cells, macrophages, and myoblasts, thereby supporting neo-myogenesis more specifically at the interface between the wound edges and the hydrogel. The selected porous DGL/PEG hydrogel acted as a guiding scaffold at the periphery of the defect, facilitating the formation and anchorage of aligned muscle fibers 21 days after injury. Overall, our results indicate DGL/PEG porous injectable hydrogel potential to create a pro-regenerative environment for muscle cells after large skeletal muscle injuries, paving the way for acellular treatment in regenerative muscle medicine.
Keywords: Volumetric muscle loss; injectable and porous hydrogels; regenerative muscle medicine.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Janssen IA N, Heymsfield SB, Wang ZM, et al.. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 yr. J Appl Physiol 2000; 89: 81–88. - PubMed
-
- Sluka KA. Gray’s anatomy - The anatomical basis of clinical practice (Chap. 5). Elsevier, 2016.
-
- Frontera WR, Ochala J. Skeletal muscle a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int 2015; 96: 183–195. - PubMed
-
- Turner NJ, Badylak S F. Regeneration of skeletal muscle. Cell Tissue Res 2012; 347: 759–774. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

