Application of privacy protection technology to healthcare big data
- PMID: 39502481
- PMCID: PMC11536567
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241282242
Application of privacy protection technology to healthcare big data
Abstract
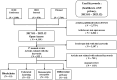
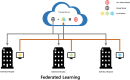
With the advent of the big data era, data security issues are becoming more common. Healthcare organizations have more data to use for analysis, but they lose money every year due to their inability to prevent data leakage. To overcome these challenges, research on the use of data protection technologies in healthcare is actively underway, particularly research on state-of-the-art technologies, such as federated learning announced by Google and blockchain technology, which has recently attracted attention. To learn about these research efforts, we explored the research, methods, and limitations of the most widely used privacy technologies. After investigating related papers published between 2017 and 2023 and identifying the latest technology trends, we selected related papers and reviewed related technologies. In the process, four technologies were the focus of this study: blockchain, federated learning, isomorphic encryption, and differential privacy. Overall, our analysis provides researchers with insight into privacy technology research by suggesting the limitations of current privacy technologies and suggesting future research directions.
Keywords: Blockchain; differential privacy; federated learning; healthcare; homomorphic encryption privacy protection.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Personal Data Protection Laws. Korean Law Information Center. https://www.law.go.kr/%EB%B2%95%EB%A0%B9/%EA%B0%9C%EC%9D%B8%EC%A0%95%EB%...
-
- General Data Protection Regulation. Intersoft consulting. https://gdpr-info.eu (accessed 5 August 2020).
-
- Hasselgren A, Kralevska K, Gligoroski D, et al. Blockchain in healthcare and health sciences—a scoping review. Int J Med Inf 2020; 134: 104040. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

