Assessing the accuracy and clinical utility of GPT-4O in abnormal blood cell morphology recognition
- PMID: 39502485
- PMCID: PMC11536573
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241298503
Assessing the accuracy and clinical utility of GPT-4O in abnormal blood cell morphology recognition
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the accuracy and clinical utility of GPT-4O in recognizing abnormal blood cell morphology, a critical component of hematologic diagnostics.
Methods: GPT-4O's blood cell morphology recognition capabilities were assessed by comparing its performance with hematologists. A total of 70 images from the Chinese National Center for Clinical Laboratories, External Quality Assessment (EQA) from 2022 to 2024 were analyzed. Two experienced hematology experts evaluated GPT-4O's recognition accuracy using a Likert scale.
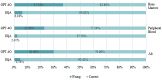
Results: GPT-4O achieved an overall accuracy of 70% in blood cell morphology recognition, significantly lower than the 95.42% accuracy of hematologists (p < 0.05). For peripheral blood smears and bone marrow smears, GPT-4O's accuracy was 77.14% and 62.86% respectively. Likert scale evaluations revealed further discrepancies, with GPT-4O scoring 288.50 out of 350, compared to higher manual scores. GPT-4O accurately recognized certain intracellular inclusions such as Howell-Jolly bodies and Auer rods, while it misidentified fragmented red blood cells as neutrophilic metamyelocytes and oval-shaped red blood cells as sickle cells. Additionally, GPT-4O had difficulty accurately identifying intracellular granules and distinguishing cell nuclei and cytoplasm.
Conclusion: GPT-4O's performance in recognizing abnormal blood cell morphology is currently inadequate compared to hematologists. Despite its potential as a supplementary tool, significant improvements in its recognition algorithms and an expanded dataset are necessary for it to be reliable for clinical use. Future research should focus on enhancing GPT-4O's diagnostic accuracy and addressing its current limitations.
Keywords: ChatGPT; GPT-4O; blood cell morphology; clinical laboratory; morphology recognition.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Imtiaz A, King J, Holmes S, et al. ChatGPT versus Bing: a clinician assessment of the accuracy of AI platforms when responding to COPD questions. Eur Respir J 2024; 63: 2400163. - PubMed
-
- Lechien JR, Naunheim MR, Maniaci A, et al. Performance and consistency of ChatGPT-4 versus otolaryngologists: a clinical case series. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2024; 170: 1519–1526. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources