Prediction of Treatment Response Based on Nutritional Status and Tumor Immunity in Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients Treated With Chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 39502617
- PMCID: PMC11534058
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10397
Prediction of Treatment Response Based on Nutritional Status and Tumor Immunity in Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients Treated With Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
Background/aim: Radiotherapy (RT) for advanced oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) is effective, especially when combined with chemotherapy (CRT). However, its success can vary depending on factors, such as tumor stage, HPV infection (p16 status), and the patient's nutritional and immune status. This study examined the controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score and tumor immunity as predictive factors for treatment outcomes in OPC, aiming to develop a personalized risk score.
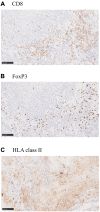
Patients and methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 84 patients with OPC treated with definitive RT or CRT, and survival outcomes were compared based on various factors, including BMI, CONUT score, CD8 expression, and HLA class II expression.
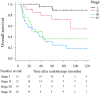
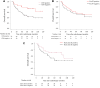
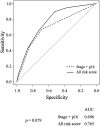
Results: We observed better overall survival (OS) rates in CD8-positive patients and those with higher HLA class II expression. The univariate analysis identified stage, p16 status, BMI, CONUT score, and CD8 expression as significantly associated with OS. In multivariate analysis, stage, BMI, and CONUT score remained significant predictors of OS. A risk scoring system was developed based on stage, p16 status, BMI, CONUT score, and CD8 expression. Patients were categorized into low-risk and high-risk groups, with significantly better survival in the low-risk group.
Conclusion: A combined risk score incorporating clinical, nutritional, and immune factors can improve the prediction of treatment outcomes for OPC patients. This risk stratification may enable personalized treatment plans and improve ΟS rates.
Keywords: CD8; CONUT score; Forkhead box P3; Human leukocyte antigen class II; Oropharyngeal cancer; body mass index; chemotherapy; radiotherapy.
©2024 The Author(s). Published by the International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures

References
-
- Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tân PF, Westra WH, Chung CH, Jordan RC, Lu C, Kim H, Axelrod R, Silverman CC, Redmond KP, Gillison ML. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(1):24–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0912217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qiu J, Yang J, Yu Y, Wang Z, Lin H, Ke D, Zheng H, Li J, Yao Q. Prognostic value of pre-therapeutic nutritional risk factors in elderly patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma receiving definitive chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11044-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruangritchankul K, Sandison A, Warburton F, Guerrero-Urbano T, Reis Ferreira M, Lei M, Thavaraj S. Clinical evaluation of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes as a prognostic factor in patients with human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2019;75(1):146–150. doi: 10.1111/his.13873. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
