Perceptual super-resolution in multiple sclerosis MRI
- PMID: 39502711
- PMCID: PMC11534588
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1473132
Perceptual super-resolution in multiple sclerosis MRI
Abstract
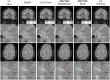
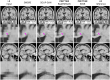
Introduction: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring of multiple sclerosis (MS) as it is used to assess lesions in the brain and spinal cord. However, in real-world clinical settings, MRI scans are often acquired with thick slices, limiting their utility for automated quantitative analyses. This work presents a single-image super-resolution (SR) reconstruction framework that leverages SR convolutional neural networks (CNN) to enhance the through-plane resolution of structural MRI in people with MS (PwMS).
Methods: Our strategy involves the supervised fine-tuning of CNN architectures, guided by a content loss function that promotes perceptual quality, as well as reconstruction accuracy, to recover high-level image features.
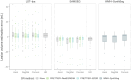
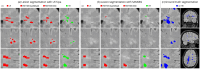
Results: Extensive evaluation with MRI data of PwMS shows that our SR strategy leads to more accurate MRI reconstructions than competing methods. Furthermore, it improves lesion segmentation on low-resolution MRI, approaching the performance achievable with high-resolution images.
Discussion: Results demonstrate the potential of our SR framework to facilitate the use of low-resolution retrospective MRI from real-world clinical settings to investigate quantitative image-based biomarkers of MS.
Keywords: CNN; MRI; deep learning; fine-tuning; lesion segmentation; multiple sclerosis; perceptual loss; super-resolution.
Copyright © 2024 Giraldo, Khan, Pineda, Liang, Lozano-Castillo, Van Wijmeersch, Woodruff, Lambin, Romero, Peeters and Sijbers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Akiba T., Sano S., Yanase T., Ohta T., Koyama M. (2019). “Optuna: a next-generation hyperparameter optimization framework,” in Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 2623–2631. 10.1145/3292500.3330701 - DOI
-
- Beirinckx Q., Jeurissen B., Nicastro M., Poot D. H., Verhoye M., den Dekker A. J., et al. . (2022). Model-based super-resolution reconstruction with joint motion estimation for improved quantitative MRI parameter mapping. Comput. Med. Imag. Graph. 100:102071. 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2022.102071 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bergstra J., Bardenet R., Bengio Y., Kégl B. (2011). “Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 24, eds. J. Shawe-Taylor, R. Zemel, P. Bartlett, F. Pereira, and K. Weinberger (Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates, Inc.),1–9.
-
- Blau Y., Mechrez R., Timofte R., Michaeli T., Zelnik-Manor L. (2019). “The 2018 PIRM challenge on perceptual image super-resolution,” in Computer Vision— ECCV 2018 Workshops, eds. L. Leal-Taixé and S. Roth (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 334–355. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

