Lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma promotes malignant potential of tumor-associated macrophages via exosomal miR-301a-3p
- PMID: 39502738
- PMCID: PMC11533007
- DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12814
Lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma promotes malignant potential of tumor-associated macrophages via exosomal miR-301a-3p
Abstract
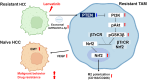
Background: The interactions between cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) via microRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial roles in malignant potential and drug resistance. However, it remains unclear how lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma (LR HCC) promotes TAM tumor biology. Here we investigated the crosstalk between LR HCC cells and TAMs for cancer progression and lenvatinib resistance, focusing on an exosomal miRNA.
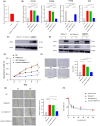
Methods: We used two bioinformatics software programs to identify miRNAs that target PTEN in gastrointestinal cancers, then investigated exosomal miRNA expression in LR HCC conditioned medium (CM). After modifying TAMs with LR HCC CM (LR TAM), macrophage phenotype and PTEN-Nrf2 signaling pathway component expression were analyzed in LR TAMs. The malignant potential and drug resistance were investigated in naïve HCC cells cultured with LR TAM CM.
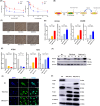
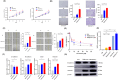
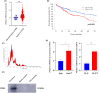
Results: LR HCC cells highly induced M2-like properties in macrophages compared with naïve HCC cells. Exosomal miR-301a-3p expression was increased in LR HCC CM, with higher activation of the PTEN/PI3K/GSK3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway in LR TAMs. Naïve HCC cells were educated with LR TAM CM to promote malignant potential and lenvatinib resistance. Inhibition of exosomal miR-301a-3p prevented the malignant potential of LR TAMs. Activation of Nrf2 signaling by LR HCC cell-derived exosomal miR-301a-3p skewed the transformation of macrophages to the M2 phenotype.
Conclusion: Our study provides new findings on the role of miR-301a-3p, suggesting it is a promising therapeutic target to improve HCC lenvatinib resistance.
Keywords: PTEN; drug resistance; exosome; hepatocellular carcinoma; lenvatinib.
© 2024 The Authors. Annals of Gastroenterological Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Japanese Society of Gastroenterological Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. received research grants from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and EPS Holdings, and scholarship donations from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AbbVie G.K., Johnson & Johnson K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors have no competing interests related to this study.
Figures
References
-
- El‐Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first‐line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 noninferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10126):1163–1173. - PubMed
-
- Zhu AX, Abbas AR, de Galarreta MR, Guan Y, Lu S, Koeppen H, et al. Molecular correlates of clinical response and resistance to atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Med. 2022;28(8):1599–1611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

