This is a preprint.
Hemifusomes and Interacting Proteolipid Nanodroplets Mediate Multi-Vesicular Body Formation
- PMID: 39502775
- PMCID: PMC11537336
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5200876/v1
Hemifusomes and Interacting Proteolipid Nanodroplets Mediate Multi-Vesicular Body Formation
Update in
-
Hemifusomes and interacting proteolipid nanodroplets mediate multi-vesicular body formation.Nat Commun. 2025 May 17;16(1):4609. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59887-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40382390 Free PMC article.
Abstract
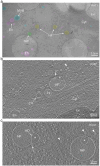
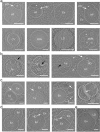
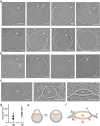
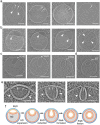
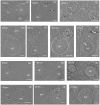
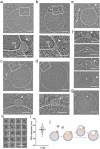
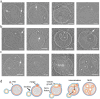
The complex, pleiomorphic membrane structure of the vesicular components within the endolysosomal system has been appreciated through decades of classical electron microscopy. However, due to the heavy fixation and staining required in these approaches, in situ visualization of fragile intermediates between early endosomes, late endosomes and ultimately multivesicular bodies (MVBs), remains elusive, raising the likelihood that other structures may have also been overlooked. Here, using in situ cryo-electron tomography in four mammalian cell lines, we discover heterotypic hemifused vesicles that share an extended hemifusion diaphragm, associated with a 42nm proteolipid nanodroplet (PND). We term this previously undescribed vesicular organelle-complex, "hemifusome". Hemifusomes make up approximately 10% of the organelle pool of the endolysosomal system, but do not participate directly in transferrin-mediated endocytosis. Hemifusomes exist in compound conformations and also contain intraluminal vesicles. Based on their range of morphologies, and the consistent presence of the PND at sites of compound hemifused vesicles, we propose that hemifusomes function as platforms for vesicular biogenesis mediated by the PND. These findings offer direct in situ evidence for a long-lived hemifusion diaphragm, and a new, ESCRT-independent model for the formation of late endosomes containing intraluminal vesicles and ultimately MVBs.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: There is NO Competing Interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

