Identifying Multiomic Signatures of X-Linked Retinoschisis-Derived Retinal Organoids and Mice Harboring Patient-Specific Mutation Using Spatiotemporal Single-Cell Transcriptomics
- PMID: 39503290
- PMCID: PMC11714187
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202405818
Identifying Multiomic Signatures of X-Linked Retinoschisis-Derived Retinal Organoids and Mice Harboring Patient-Specific Mutation Using Spatiotemporal Single-Cell Transcriptomics
Abstract
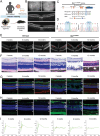
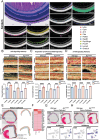
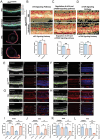
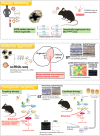
X-linked retinoschisis (XLRS) is an inherited retinal disorder with severe retinoschisis and visual impairments. Multiomics approaches integrate single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) and spatiotemporal transcriptomics (ST) offering potential for dissecting transcriptional networks and revealing cell-cell interactions involved in biomolecular pathomechanisms. Herein, a multimodal approach is demonstrated combining high-throughput scRNA-seq and ST to elucidate XLRS-specific transcriptomic signatures in two XLRS-like models with retinal splitting phenotypes, including genetically engineered (Rs1emR209C) mice and patient-derived retinal organoids harboring the same patient-specific p.R209C mutation. Through multiomics transcriptomic analysis, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress/eukryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2) signaling, mTOR pathway, and the regulation of eIF4 and p70S6K pathways are identified as chronically enriched and highly conserved disease pathways between two XLRS-like models. Western blots and proteomics analysis validate the occurrence of unfolded protein responses, chronic eIF2α signaling activation, and chronic ER stress-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, therapeutic targeting of the chronic ER stress/eIF2α pathway activation synergistically enhances the efficacy of AAV-mediated RS1 gene delivery, ultimately improving bipolar cell integrity, postsynaptic transmission, disorganized retinal architecture, and electrophysiological responses. Collectively, the complex transcriptomic signatures obtained from Rs1emR209C mice and patient-derived retinal organoids using the multiomics approach provide opportunities to unravel potential therapeutic targets for incurable retinal diseases, such as XLRS.
Keywords: X‐link retinoschisis (XLRS); chronic ER stress‐associated apoptosis; eIF2α signaling; genetically engineered mice; retinoschisin 1 (RS1); single‐cell RNA‐sequencing; spatiotemporal transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- a) Sauer C. G., Gehrig A., Warneke‐Wittstock R., Marquardt A., Ewing C. C., Gibson A., Lorenz B., Jurklies B., Weber B. H., Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 164; - PubMed
- b) Zeng Y., Takada Y., Kjellstrom S., Hiriyanna K., Tanikawa A., Wawrousek E., Smaoui N., Caruso R., Bush R. A., Sieving P. A., Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004, 45, 3279. - PubMed
-
- a) Weber B. H., Schrewe H., Molday L. L., Gehrig A., White K. L., Seeliger M. W., Jaissle G. B., Friedburg C., Tamm E., Molday R. S., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 6222; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Kjellstrom S., Bush R. A., Zeng Y., Takada Y., Sieving P. A., Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007, 48, 3837; - PubMed
- c) Liu M., Liu J., Wang W., Liu G., Jin X., Lei B., Front Med. 2022, 9, 886947. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Ou J., Vijayasarathy C., Ziccardi L., Chen S., Zeng Y., Marangoni D., Pope J. G., Bush R. A., Wu Z., Li W., Sieving P. A., J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 2891,; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Bush R. A., Zeng Y., Colosi P., Kjellstrom S., Hiriyanna S., Vijayasarathy C., Santos M., Li J., Wu Z., Sieving P. A., Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 376,; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Zeng Y., Petralia R. S., Vijayasarathy C., Wu Z., Hiriyanna S., Song H., Wang Y. X., Sieving P. A., Bush R. A., Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016, 57, OCT277,. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 113-2321-B-A49-011/National Science and Technology Council
- 113-2321-B-A49-013/National Science and Technology Council
- MOHW113-TDUB-211-114007/Ministry of Health and Welfare
- V112E-002-4/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V112C-135/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V113B-010/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V113C-125/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V113C-181/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V113E-005-1/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- CI-113-18/Yen Tjing Ling Medical Foundation
- 113VACS-007/the Veterans Affairs Council
- VGHUST113-G1-5-1/VGHUST Joint Research Program
- VN113-10/TVGH-NTUH Joint Research Program
- VTA113-V1-3-1/VGH, TSGH, AS Joint Research Program
- IBMS-CRC112-P03/the IBMS CRC Research Program of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taiwan
- 112W031101/Ministry of Education (MOE)
- 113W031101/Ministry of Education (MOE)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
