Extensive import of nucleus-encoded tRNAs into chloroplasts of the photosynthetic lycophyte, Selaginella kraussiana
- PMID: 39503889
- PMCID: PMC11573648
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2412221121
Extensive import of nucleus-encoded tRNAs into chloroplasts of the photosynthetic lycophyte, Selaginella kraussiana
Abstract
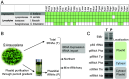
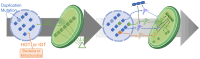
Over the course of evolution, land plant mitochondrial genomes have lost many transfer RNA (tRNA) genes and the import of nucleus-encoded tRNAs is essential for mitochondrial protein synthesis. By contrast, plastidial genomes of photosynthetic land plants generally possess a complete set of tRNA genes and the existence of plastidial tRNA import remains a long-standing question. The early vascular plants of the Selaginella genus show an extensive loss of plastidial tRNA genes while retaining photosynthetic capacity, and represent an ideal model for answering this question. Using purification, northern blot hybridization, and high-throughput tRNA sequencing, a global analysis of total and plastidial tRNA populations was undertaken in Selaginella kraussiana. We confirmed the expression of all plastidial tRNA genes and, conversely, observed that nucleus-encoded tRNAs corresponding to these plastidial tRNAs were generally excluded from the chloroplasts. We then demonstrated a selective and differential plastidial import of around forty nucleus-encoded tRNA species, likely compensating for the insufficient coding capacity of plastidial-encoded tRNAs. In-depth analysis revealed differential import of tRNA isodecoders, leading to the identification of specific situations. This includes the expression and import of nucleus-encoded tRNAs expressed from plastidial or bacterial-like genes inserted into the nuclear genome. Overall, our results confirm the existence of molecular processes that enable tRNAs to be selectively imported not only into mitochondria, as previously described, but also into chloroplasts, when necessary.
Keywords: RNA trafficking; evolution; gene transfer; oorganelle; plant.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Warren J. M., Sloan D. B., Interchangeable parts: The evolutionarily dynamic tRNA population in plant mitochondria. Mitochondrion 52, 144–156 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Cognat V., Pawlak G., Pflieger D., Drouard L., PlantRNA 2.0: An updated database dedicated to tRNAs of photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plant J. 112, 1112–1119 (2022). - PubMed
-
- dePamphilis C. W., Palmer J. D., Loss of photosynthetic and chlororespiratory genes from the plastid genome of a parasitic flowering plant. Nature 348, 337–339 (1990). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

