Food for thought: Nutrient metabolism controlling early T cell development
- PMID: 39504233
- PMCID: PMC11662157
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.202400179
Food for thought: Nutrient metabolism controlling early T cell development
Abstract
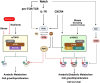
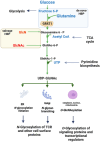
T cells develop in the thymus by expressing a diverse repertoire of either αβ- or γδ-T cell receptors (TCR). While many studies have elucidated how TCR signaling and gene expression control T cell ontogeny, the role of nutrient metabolism is just emerging. Here, we discuss how metabolic reprogramming and nutrient availability impact the fate of developing thymic T cells. We focus on how the PI3K/mTOR signaling mediates various extracellular inputs and how this signaling pathway controls metabolic rewiring during highly proliferative and anabolic developmental stages. We highlight the role of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway that generates metabolites that are utilized for N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins and how it impacts TCR expression during T cell ontogeny. We consider the dichotomy in metabolic needs during αβ- versus γδ-T cell lineage commitment as well as how metabolism is also coupled to molecular signaling that controls cell fate.
Keywords: PI3K/mTOR signaling; glycosylation; hexosamine biosynthesis; mTORC1/mTORC2; nutrient metabolism; thymic T cell development; αβ‐ and γδ‐T cells.
© 2024 The Author(s). BioEssays published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chevalier, P. , Sevilla, R. , Zalles, L. , Sejas, E. , Belmonte, G. , Parent, G. , & Jambon, B. (1996). Immuno‐nutritional recovery of children with severe malnutrition. Sante, 6, 201–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

