An oral non-covalent non-peptidic inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro ameliorates viral replication and pathogenesis in vivo
- PMID: 39504242
- PMCID: PMC12180444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114929
An oral non-covalent non-peptidic inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro ameliorates viral replication and pathogenesis in vivo
Abstract
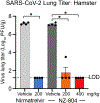
Safe, effective, and low-cost oral antiviral therapies are needed to treat those at high risk for developing severe COVID-19. To that end, we performed a high-throughput screen to identify non-peptidic, non-covalent inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), an essential enzyme in viral replication. NZ-804 was developed from a screening hit through iterative rounds of structure-guided medicinal chemistry. NZ-804 potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Mpro (0.009 μM IC50) as well as SARS-CoV-2 replication in human lung cell lines (0.008 μM EC50) and primary human airway epithelial cell cultures. Antiviral activity is maintained against distantly related sarbecoviruses and endemic human CoV OC43. In SARS-CoV-2 mouse and hamster disease models, NZ-804 therapy given once or twice daily significantly diminished SARS-CoV-2 replication and pathogenesis. NZ-804 synthesis is low cost and uncomplicated, simplifying global production and access. These data support the exploration of NZ-804 as a therapy for COVID-19 and future emerging sarbecovirus infections.
Keywords: CP: Microbiology; Paxlovid; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; broad-spectrum; coronavirus; emerging viruses; protease; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.C.S., S.T., X.B., I.V.K., J.L.W., N.E.Z., M.K.P., A.A., P.K.J., R.B., A.F., and Z.S. are listed as inventors on a patent for NZ-804. R.S.B. is a member of the advisory boards of VaxArt and Invivyd and has collaborations with Takeda, Pfizer, Moderna, Ridgeback Biosciences, Gilead, and Eli Lily. Y.K. has received unrelated funding support from Daiichi Sankyo Pharmaceutical, Toyama Chemical, Tauns Laboratories, Inc., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical, KM Biologics, Kyoritsu Seiyaku, Shinya Corporation, and Fuji Rebio.
Figures




References
-
- Hlávka J. (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- SRA/PRJNA1061174
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

