Resistance profiles of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in a large centre in England: are we already losing cefiderocol?
- PMID: 39504496
- PMCID: PMC11695913
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkae367
Resistance profiles of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in a large centre in England: are we already losing cefiderocol?
Abstract
Background: Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) pose difficult therapeutic challenges. We aimed to characterize antimicrobial resistance profiles of CPE in our centre.
Methods: All non-duplicate CPE isolates between 1 August 2020 and 31 August 2023 in a large teaching trust in England were retrospectively studied. Cefiderocol antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) was performed using disc diffusion, ceftazidime/avibactam using disc diffusion and gradient diffusion, and ceftazidime/avibactam aztreonam synergy using the double disc diffusion method. EUCAST version 14.0 breakpoints were used.
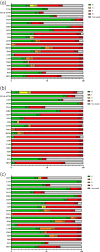
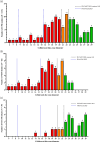
Results: A total of 158 CPE from 136 patients were isolated. Most patients were colonized with CPE, but only 16.9% had active infections. Thirty-day all-cause mortality was 10.3%, increasing to 13% for patients with infections and to 18.2% for bacteraemias. OXA-48 was the most prevalent carbapenemase (48.1%), followed by NDM (38%). All isolates exhibited MDR profiles, with high levels of resistance to meropenem (41.1%). Resistance to cefiderocol was found in 69.7% of NDM-producing isolates, with a further 18.2% in the area of technical uncertainty. Ceftazidime/avibactam and aztreonam synergy was seen in 87.5% of isolates, whereas colistin and fosfomycin susceptibility remained high (98.1% and 97.2%, respectively). All OXA-48-producing isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime/avibactam, and 15.3% were resistant to cefiderocol. No patients had been exposed to cefiderocol beforehand, whereas three had been exposed to ceftazidime/avibactam. The most common risk factor for CPE isolation was travel and receiving healthcare abroad, especially in Asia.
Conclusions: We found high rates of resistance to cefiderocol in CPE isolates without prior cefiderocol exposure. Our results prohibit empirical use of cefiderocol for the treatment of CPE infections in our setting.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on: Resistance profiles of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in a large centre in England: are we already losing cefiderocol?J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 May 2;80(5):1462-1464. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaf060. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40068836 No abstract available.
-
Comment on: Resistance profiles of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in a large centre in England: are we already losing cefiderocol?J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 May 2;80(5):1465-1468. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaf074. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40068838 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ramos-Castañeda JA, Ruano-Ravina A, Barbosa-Lorenzo R et al. Mortality due to KPC carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: systematic review and meta-analysis: mortality due to KPC Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. J Infect 2018; 76: 438–48. 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.02.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- CLSI . Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing—Thirty-second Edition: M100. 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

